Net rate, English is P/B Ratio, or P/BV Ratio By comparing the market price of the stock and the company’s tangible assets, the current stock price is higher than the actual asset value of the company.
Like other indicators, the net ratio of the market has a relatively accurate price comparison function within a certain range.However, the municipal net ratio also has its own limitations.What are the aspects of attention when investors use a net ratio to judge stocks?
Bleak American broker:Ying Diandai 劵| | Futu Moomoo| | Microex Securities| | Tiger securities| | First securities| | Robinhood in
Directory of this article
- What is the net ratio?What is the English ratio English?
- Which industries are suitable for the city’s net ratio?
- How to view the company’s water net ratio?
- How to use a net rate of municipality to evaluate stocks?
- How much is the city’s net ratio?
- Is the water net ratio high or good?
- The difference between the net ratio and the price-earnings ratio
- Municipal net ratio comparison of various industries in the United States
- common problem
- More company valuation
What is the net ratio?What is the English ratio English?
Municipal net rate is mainly used to study the ownership of listed companies Physical asset(ASSETS) and share price Relationship between (Stock Price).The calculation method is as follows:
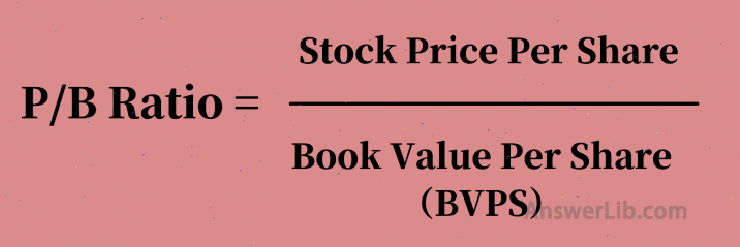
Among them, Book Value Per Share, referred to as BVPS, the calculation method is as follows:
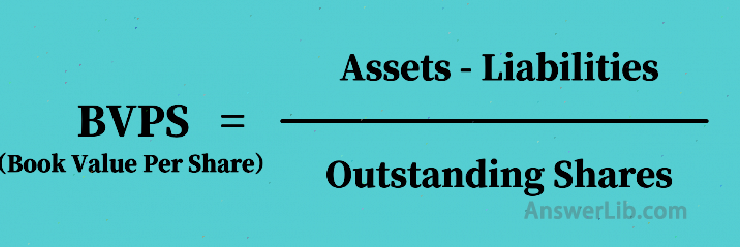
The ASSETS here is the company’s total physical asset, Liabilities refers to the company’s debt, and Outstanding Shares is the total number of shares issued by the company.
Notice: BOOK VALUE here mainly refers to the company’s tangible asset, such as real estate, machinery and equipment, and excluding intangible assets such as patents.
For example: Company A, its total tangible asset value is US $ 30 billion and total liabilities are US $ 2 billion.At present, there are 100 million shares on the market.The current stock price is $ 15/share.So:
- Company A’s net assets from 3 billion to 20 billion = $ 1 billion
- Its BVPS is $ 1 billion/100 million circulation stock = $ 10/share
- Its market ratio is 15/10 = 1.5 (times), that is, Company A’s stock price is 1.5 times that of its book assets.
The significance of this comparison is that the stock price is a forward-looking indicator for the company’s future cash flow.Net assets are accounting measurements based on the principle of historical cost based on the principle of historical costs.
P/B Ratio considers the company’s past stock issuance situation, considers all profits or losses, minus dividend and stock repurchase, that is, the part of the funds that need to be paid to shareholders in the income.
However, Book Value does not represent the actual value of the company because it does not include intangible assets such as patents and trademarks.
At the same time, the net ratio of the municipal ratio does not include the shares of the net assets, because when the denominator is negative, this comparison is meaningless.
When investors want to analyze the stock price, the market ratio is a very good tool.When comparing two stocks with similar growth and profitability, the price-earnings ratio can also be used to determine which stock is more investment value.
Theoretically, the high net net ratio indicates that the price of the stock exceeds the actual value of the company’s assets, while the low net net ratio indicates that the stock price is very cheap, and its value is usually better, but this varies from the industry.
Which industries are suitable for the city’s net ratio?
A.Inconsistent yield industry
Because the municipal net ratio focuses on the company’s tangible asset instead of income, the municipal net ratio is a particularly useful indicator for industry companies with inconsistent income.
For example, the income of many bank stocks is extremely inconsistent.It is more impossible to obtain accurate and valuable results through the yield P/E.At this time, the net rate of the municipal ratio can more clearly reflect the relative value of these companies.
B.Industry focusing on physical assets
Because the net ratio of the municipal ratio is the value of tangible assets, it is very suitable for the stock price analysis of companies such as construction, manufacturing and other industries, because the net assets used by P/B are prices based on accounting standards*, and the accounting standards do not recognize the brandValue and other intangible assets tend to adopt conservative cost capitalization methods.
Therefore, when using a net ratio of a municipal ratio to determine the company’s stocks that are mainly intangible assets, the P/B value is very high due to its high stock price and very low net asset value, losing the meaning of the P/B value.For example, most of the asset value of Microsoft is determined by its intellectual property rather than physical assets.Therefore, Microsoft’s stock value has nothing to do with its net assets, and P/B Ratio cannot measure its price.
*Accounting Standards -General Accepted Accounting Principles, referred to as GAAP, by the Financial Accounting Standard Committee (Financial Accounting Standards Board ( FSAB)release.
C.Periodic industry
In addition, the municipal net ratio also has a good guidance value for the cyclical industry’s stocks.Such stocks have risen during the economic prosperity period, and the economic recession declines.The company’s stock price is determined by the market supply and demand relationship.To a certain role, such as tourism, entertainment, and luxury retail.
Due to the relatively stable cost of P/B Ratio in this type of industry, the P/B value can more intuitively reflect the company’s current stock price relatively high or low.
How to view the company’s water net ratio?
The stock market price in the market ratio is public information, and the company’s physical asset information will be displayed in regular corporate information disclosure.ThereforeInvestors provide information guidance.
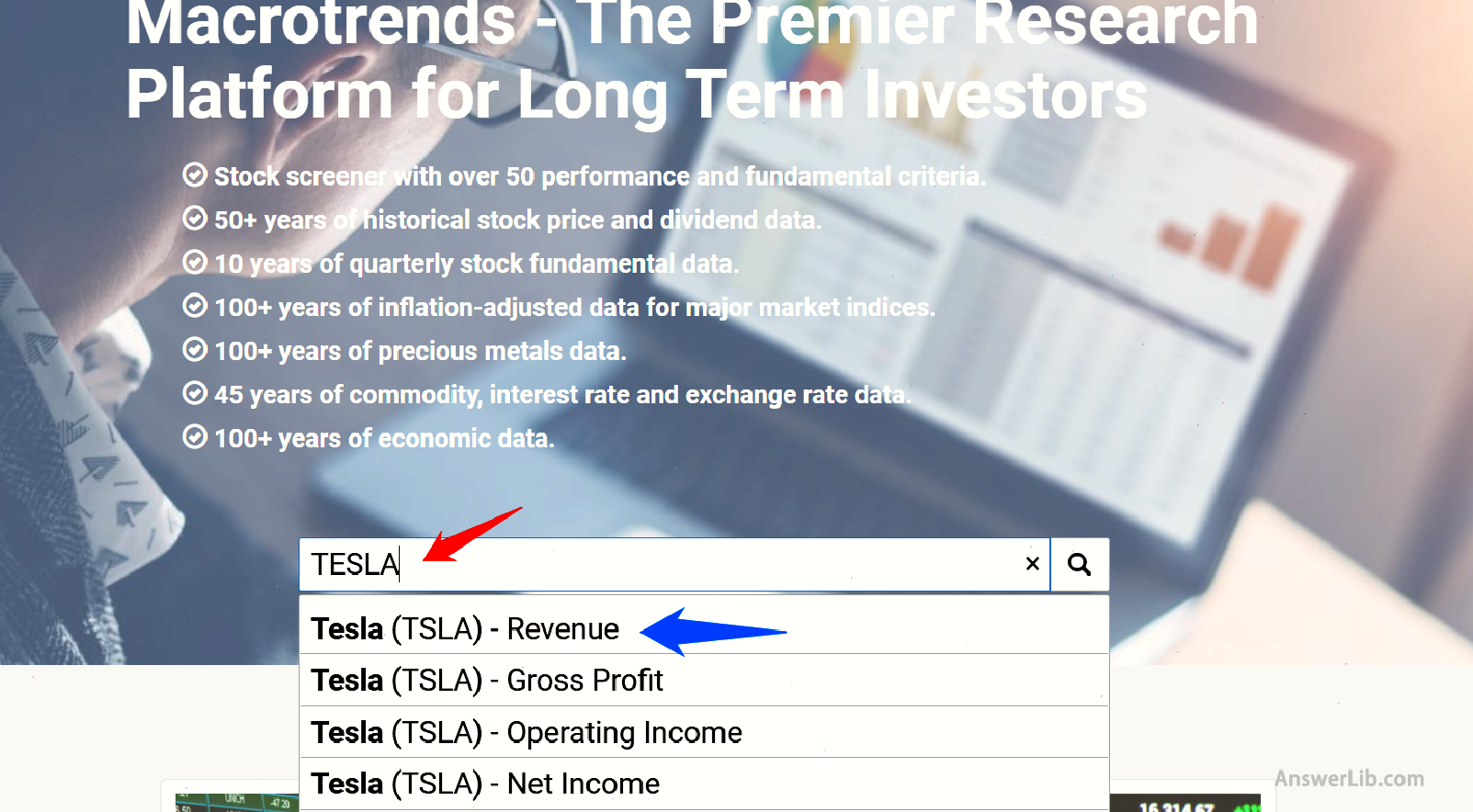
step one: Enter the homepage of Macrotrends and enter the target stock name or code in the search box.At the same time, select the “Revenue” option in the drop-down menu.For example, we search for Tesla.
Step 2: In the option, select “Price Ratios”, and then select “Price/Book Ratio”.
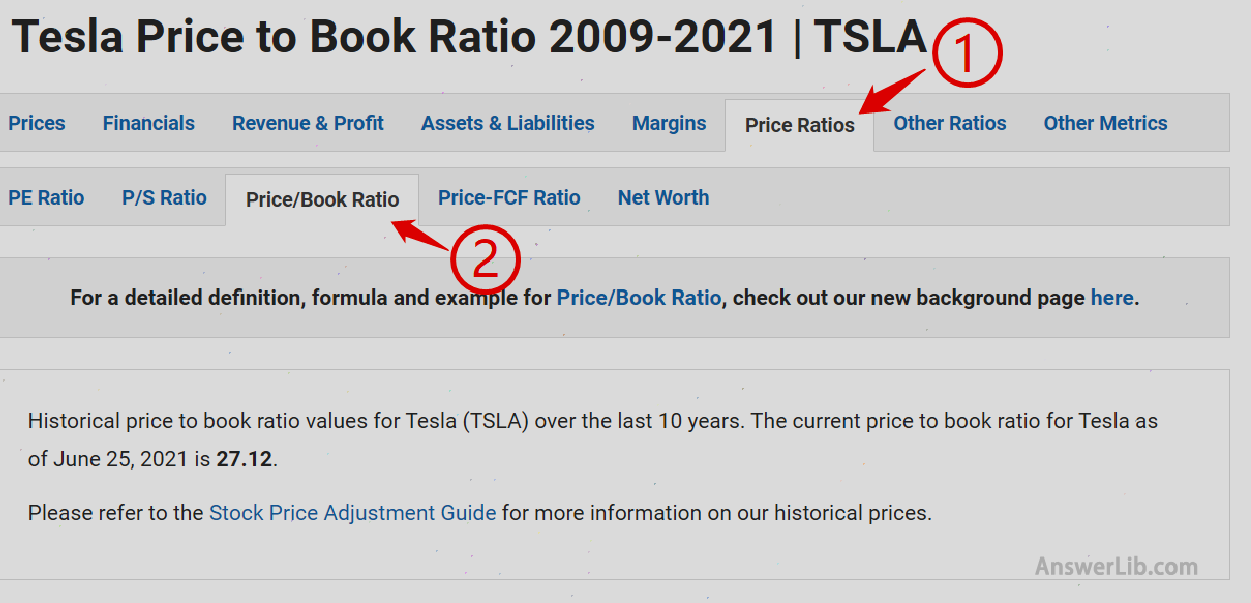
Step 3: Continue to scroll the page to check the net ratio data of Tesla, you can choose 1 year, 2 years, 3 years, 5 years, or all knowing years.Here, take all the years of knowing as an example:
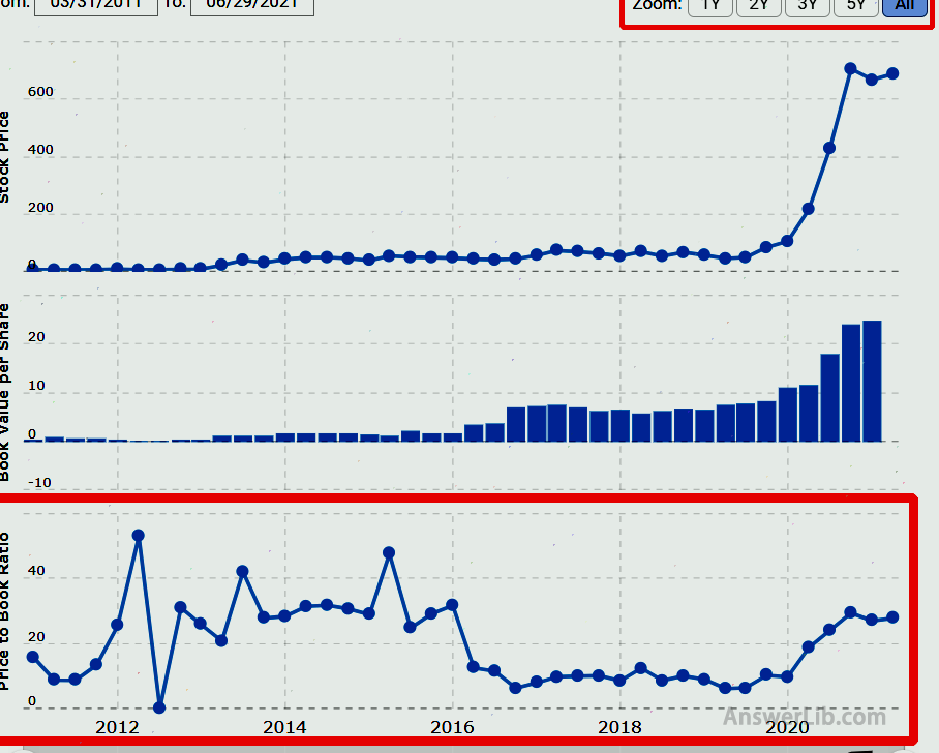
In this way, you can find Tesla’s P / E ratio historical data, and the current data is from March 28, 2011 to June 28, 2021.
How to use a net rate of municipality to evaluate stocks?
Although the water net ratio has not considered factors such as future profit prospects or intangible assets, it cannot evaluate companies that are mainly intangible assets.
However, the water net ratio can be used to determine the stock price of the stock price soaring but without specific assets.Because when the stock price is soaring, general investors will think that the company’s operation is good, but when viewing the P/B value, it is found that the company’s net asset value has not increased accordingly, that is, the company’s stock suddenly increases without the company’s capital increase., It may be an important signal for stock prices to be hyped.
In addition, in order to better understand the valuation of a company, investors should use it with the ROE (ROE)*indicator, which is a reliable growth indicator.
*Roe, the full name is Return On Equity, which refers to the “net asset return rate”.The calculation method is as follows:
Return rate of net assets = Net Profit / Shareholder Equity
The Net Profit here refers to the profit after the company’s expenses, but the profit here is the profit before Dividend.And Shareholder Equity = Asset -Liability, Equity here includes tangible assets, as well as intangible assets, such as intellectual property rights, etc.
Because shareholders’ income is equal to the company’s assets’ debt, ROE is regarded as the return on net assets of shareholders, and is considered an indicator to measure the profitability of a company’s equity relative to shareholders’ equity.The higher the ROE, the stronger the profitability.
For example, in the past five years, Bank of America The water net ratio has always been lower than JPMorgan But this does not necessarily mean that Bank of America is “cheaper”.In fact, the ROE of JP Morgan Chase has always been higher than the Bank of America.
If there is a huge difference between the P/B value and the ROE value, it is usually regarded as the danger signal of the company, because if the ROE value of a company increases, its P/B value should also increase.The overestimated growth stocks often show a combination of low ROE value and high-city net ratio.
How much is the city’s net ratio?
A.For industries dominated by tangible assets
For companies focusing on tangible assets, the price-earnings ratio usually has 1 and 3 benchmark values:
- When the municipal net rate is lower than 1, it is usually considered a good P/B value, indicating that the stock price of the stock is lower than its net asset value.In the future, there is a good room for rising, or the current stock is undervalued, which is more suitable for investors to buy it.Entry holding.
- When the municipal net ratio is higher than 3, it indicates that the current stock price is three times the net asset value.The stock price reaches a certain height, the rise in the rise is limited, or the stock price is overestimated.For investors, it can take a moderate watch attitude.
B.For industries dominated by intangible assets
For companies that are dominated by intangible assets, for example, technology companies such as Facebook are not useless.
Through the overall market situation of the relevant industry for a period of time, the operation of a listed company is good, development, problems, and revenue decline.
For example, from 2010 to 2020, the average market ratio of technology companies listed on the Nasdaq Stock Exchange rose steadily, which was doubled during this period.
Therefore, although the value of the municipal net rate in the technology company industry is often too high, and the significance of the evaluation is lost, by analyzing the changes in the historical market ratio of a company, or the comparison of the net ratio of different companies, you can also obtain reference value with reference valueinformation.
Is the water net ratio high or good?
1.What does the low-market net rate explain?
Due to the calculation method of the net ratio of the municipal ratio, for traditional industries, the lower the market ratio that often means that the “cheaper” the stock price is, the time it is worth starting.
Especially when the net ratio of the municipality is less than 1, it means that its transaction price is lower than the value of its assets, and it is a good municipal net ratio in the tangible asset industry.Buying company shares at a price below net assets can create “safe margins” for value investors.
However, the low market ratio is not necessarily an indicator worth investing.
First of all, the value of net assets is not necessarily equal to the value of the enterprise.Most enterprises’ net assets of net assets are lower than their disclosed net asset value, because when some enterprises are sold or liquidated, many factory equipment or other tangible assets have depreciated sharply.Essence
This leads to the net rate of net assets when calculating the net ratio of the city, because the high net assets make the net ratio low, but in essence, the company’s real assets have not disclosed the net asset value.
Secondly, the low net net ratio may show that the company’s own assets do not make money, and investors have unintentionally invested, so low stock prices have led to a lower net ratio.
In summary, investors cannot blindly pursue low-market net ratios, and need to carefully identify the true quality of the company’s net assets, and combine indicators such as ROE to determine whether the net assets can continue to make profit.
2.What does the high city net rate explain?
The net rate of high cities usually means that its stock price is higher than the company’s book price, which may show two situations:
- First, the company operates well, has obtained market recognition, attracts many investors, has risen in stock prices, and the net rate of market ratios has risen.But investors also need to pay attention that the stock of high-municipal net ratios may mean that the rise of the rise is being compressed;
- Second, the stock price is overestimated, or it is raised by malicious speculation;
Like the low-market net ratio, it is impossible to judge the authenticity of the value of a stock by relying on the height of the municipal net ratio alone, although the low-city net ratio is better than the high-city net ratio.
In summary, you often need to combine the historical data of the municipal net rate for a period of time, or other comparative indexes to comprehensively analyze the true value of a stock.
The difference between the net ratio and the price-earnings ratio
IThe ratio of the ratio is different
- Municipal net ratio, which is used to compare the company’s book assets per share, that is, asset-liabilities, indicates the relationship between the stock price and the company’s tangible assets.
- P / E ratio It is used to compare the company’s earnings per share, indicating the relationship between the stock price and the company’s profit and loss.
II.Suitable for different industries
- The water net ratio is very suitable for valuations of banks or financial service companies, because the higher the net assets of such companies, the higher the ability to create value, the company’s stock price will rise.The rate can be reflected very well.
- The price-earnings ratio is suitable for the consumer goods industry companies such as food, medical care, and public services.These industries are weak and cyclical industries.They are less affected by the market economy.It is more suitable to use P / E ratio to reflect the operating situation and the value of the stock price.
III.The company’s assets are different
- Municipal net rate is suitable for companies that hold tangible assets
- P / E ratio has basically no requirements for the company’s asset type
Related Reading:What is the P/E RATIO: Is the low-priced stock cheap?
Municipal net ratio comparison of various industries in the United States
industry | Number of companies in the industry | P/E ratio (P/B Ratio) | Return rate of net assets (ROE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advertising | 61 | 5.73 | 2.93% |
| Aerospace/defense | 72 | 4.44 | 8.54% |
| Air Transport | 17 | 3.22 | -47.03% |
| Apparel | 51 | 4.11 | -8.19% |
| Auto & Truck | 19 | 7.58 | 4.49% |
| Auto Parts | 52 | 4.78 | -14.31% |
| Bank (Money Center) | 7 | 1.00 | 7.41% |
| Banks (Regional) | 598 | 1.08 | 8.22% |
| Beverage (alcoholic) | twenty three | 3.45 | 10.10% |
| Beverage (soft) | 41 | 8.50 | 28.86% |
| Broadcasting | 29 | 1.58 | 0.24% |
| Brokerage & Investment Banking | 39 | 1.52 | 12.08% |
| Building Materials | 42 | 4.98 | 20.54% |
| Business & Consumer Services | 169 | 5.85 | 6.81% |
| Cable TV | 13 | 3.13 | 11.47% |
| Chemical (BASIC) | 48 | 2.96 | -1.82% |
| Chemical (DIVERSIFIED) | 5 | 2.18 | 13.25% |
| Chemical (Specialty) | 97 | 3.10 | 2.50% |
| Coal & Related Energy | 29 | 1.36 | -41.66% |
| Computer service | 116 | 4.00 | 13.50% |
| Computers/Peripherals | 52 | 22.90 | 50.53% |
| Construction support | 46 | 3.82 | 13.20% |
| DIVERSIFIED | 29 | 1.86 | 10.62% |
| Drags (biotechnology) | 547 | 7.18 | -1.19% |
| Drugs (PHARMACEUTICAL) | 287 | 5.04 | 18.98% |
| Education | 38 | 2.92 | -5.66% |
| Electrical Equipment | 122 | 6.28 | 17.67% |
| Electronics (consumer & office) | twenty two | 4.26 | -4.89% |
| Electronics (General) | 157 | 4.14 | 6.67% |
| Engineering/Construction | 61 | 2.32 | 2.54% |
| Entertainment | 118 | 5.49 | -2.87% |
| Environmental & Waste Services | 86 | 4.68 | 6.21% |
| Faring/agriculture | 32 | 3.21 | 14.03% |
| Financial svcs.(Non-BANK & Insurance) | 235 | 2.23 | 64.28% |
| Food Processing | 101 | 2.57 | 10.12% |
| FOOD WHOLESALERS | 18 | 5.02 | -5.03% |
| Furn/home furnishings | 40 | 2.68 | 13.37% |
| Green & Renewable Energy | 25 | 1.68 | -20.59% |
| Healthcare Products | 265 | 5.77 | 10.55% |
| Healthcare Support Services | 129 | 2.91 | 16.60% |
| Healthcare Information and Technology | 139 | 7.12 | 14.11% |
| Homebuilding | 30 | 1.75 | 17.70% |
| HOSPITALS/HealthCare Facilities | 32 | 5.78 | 70.64% |
| Hotel/Gaming | 66 | 6.10 | -30.40% |
| Household Products | 140 | 9.06 | 31.60% |
| Information Services | 77 | 8.38 | 14.35% |
| Insurance (general) | twenty one | 1.45 | 1.49% |
| Insurance (Life) | 26 | 0.59 | 5.61% |
| Insurance (PROP/CAS.) | 55 | 1.54 | 9.19% |
| Investments & Asset Management | 348 | 2.05 | 12.35% |
| Machinery | 125 | 4.55 | 12.65% |
| Metals & Mining | 86 | 3.29 | 2.67% |
| Office Equipment & Services | twenty two | 2.60 | 6.36% |
| OIL/GAS (Integrated) | 3 | 1.05 | -6.19% |
| OIL/GAS (Production and Exploration) | 278 | 1.21 | -37.09% |
| Oil/Gas Distribution | 57 | 1.24 | 1.28% |
| Oilfield SVCS/EQUIP. | 135 | 1.30 | -26.63% |
| Packaging & Container | 26 | 3.76 | 9.76% |
| Paper/Forest Products | 15 | 1.61 | 4.69% |
| POWER | 55 | 1.90 | 7.69% |
| Precious metals | 93 | 2.19 | 8.27% |
| Publishing & newSpapers | 29 | 2.07 | -14.18% |
| R.E.I.T. | 238 | 2.11 | 2.17% |
| Real Estate (Development) | 25 | 1.19 | -0.13% |
| Real Estate (General/DIVERSIFIED) | 11 | 1.19 | 2.00% |
| Real Estate (Operations & Services) | 61 | 3.21 | 4.71% |
| Recuction | 69 | 10.37 | -7.19% |
| Reinsurance | 2 | 0.75 | 2.42% |
| Restaurant/dining | 79 | Na | Na |
| Retail (Automotive) | 30 | 5.99 | 36.28% |
| Retail (Building Supply) | 15 | 40.07 | 0.27% |
| Retail (Distributors) | 85 | 3.39 | 9.67% |
| Retail (general) | 17 | 5.43 | 20.64% |
| Retail (Grocery and Food) | 14 | 2.51 | 30.63% |
| Retail (online) | 75 | 18.62 | 27.05% |
| Retail (SPECIAL LINES) | 85 | 5.51 | -0.64% |
| Rubber & Tires | 3 | 1.04 | -25.69% |
| Semiconductor | 70 | 6.87 | 22.13% |
| Semiconductor Equip | 40 | 7.87 | 32.23% |
| Shipbuilding & marine | 11 | 1.13 | -5.70% |
| Shoe | 11 | 14.87 | 23.70% |
| Software (Entertainment) | 101 | 6.23 | 17.71% |
| Software (Internet) | 36 | 15.19 | -11.23% |
| Software (System & Application) | 388 | 14.07 | 28.09% |
| Steel | 32 | 1.55 | -2.84% |
| Telecom (Wireless) | 16 | 2.36 | 8.91% |
| Telecom.Equipment | 96 | 4.84 | 17.10% |
| Telecom.Services | 58 | 1.73 | 11.27% |
| Tobacco | 15 | Na | -0.23% |
| Transportation | twenty one | 6.77 | 22.77% |
| Transportation (railroids) | 6 | 5.82 | 21.47% |
| Trucking | 35 | 4.81 | -17.70% |
| Utility (general) | 16 | 1.84 | 7.49% |
| Utility (Water) | 17 | 3.51 | 8.25% |
| Total Market | 7582 | 3.81 | 8.25% |
Data Sources:Price and value to book ratio by sector (US)
common problem
Question 1: What is the English ratio English?The English rate English English is Price-to-Book-Value Ratio, referred to as P/B Ratio, or PBR.It is mainly to study the relationship between the physical assets (assets) owned by listed companies and the stock price.
See More
Municipal net ratio is suitable for industries mainly based on tangible assets.The price-earnings ratio usually has two benchmark values of 1 and 3.When the market ratio is lower than 1, it means that the stock price of the stock is lower than its net asset value.Rising space, or current stocks are underestimated, more suitable for investors to buy holding; when the water net ratio is higher than 3, it means that the current stock price is three times the net asset value.Or the stock price is overestimated, for investors to take a moderate watching attitude.
See More
Due to the calculation method of the net ratio of the municipal ratio, for traditional industries, the lower the market ratio that often means that the “cheaper” the stock price is, the time it is worth starting.Gaomi net ratio usually means that its stock price is higher than the company’s book price.
However, investors cannot blindly pursue low-market net ratios, and they need to carefully identify the true quality of the company’s net assets, and combine indicators such as ROE to determine whether the net assets can continue to make profits.
See More
There are several differences between the city’s net ratio and P / E ratio:
1) Municipal net ratio is used to compare the relationship between the stock price and the company’s tangible assets; while the price-earnings ratio is used to represent the relationship between the stock price and the company’s profit and loss;
2) Municipal net ratio is very suitable for valuation of banks or financial service companies; the price-earnings ratio is suitable for the valuation of consumer goods industry companies such as food, medical care, and public services;
3) Municipal net ratio is suitable for companies to hold tangible assets; the price-earnings ratio basically does not require the company’s asset type
See More
More company valuation
- Julian Roberts – Julian Robertson: Father of Tiger Baby
- Explore the 24 first-level dealers of the Federal Reserve
- Important Finance and Investment News
- What is a corporate value multiple?Enterprise Multiple
- What is preferred stock?Preferred stock
- What is the operating leverage coefficient?Degree of Operating Leverage
- What is debt repayment payment rate?DEBT Service Coverage Ratio
- What is capital expenditure?Capital Expendital
- What is the capital asset pricing model?Capital Asset Pricing Model
- What is financial leverage coefficient? Degree of Financial Leverage
