Balance sheet It is one of the company’s important financial statements, and its importance is to reflect the company’s assets, debt status, and shareholders’ equity at a certain time.
By comparing with the company’s previous asset-liability statements, the company’s assets, debt, and shareholders ‘equity growth or reduction of shareholders’ equity will be analyzed.Asset liabilities and liabilities Profits and Cash flow sheet It is the most important financial statement and the analysis foundation for investment decisions.So, what data do you mainly include the balance sheet and how to understand the balance sheet?
Bleak American broker:Ying Diandai 劵| | Futu Moomoo| | Microex Securities| | Tiger securities| | First securities| | Robinhood in
Directory of this article
- What is the balance sheet?
- What are the components of the balance sheet?
- How to understand the balance sheet?
- What financial information can I read from the balance sheet?
- What is the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet?
- How to understand the Fed’s balance sheet?
- Fed’s asset-liability trend chart
- American Langshang Daquan
- More company valuation
What is the balance sheet?
Asset-liability statement English is Balance Sheet, sometimes also called the “financial status table”, and the corresponding English is statement of Financial Position), which shows that the company’s financial situation on a certain date is the most important thing when understanding the company’s financial status.One of the reference data tables is also one of the three major accounting statements.The asset-liability statement reflects the company’s total asset value, total liabilities and total shareholder equity of the company, which indicates the current economic resources that the company currently owns or controlled, the current obligations assumed, and the owner’s requirements for net assets for net assetsright.
In terms of form, there are two main forms of balance sheets: vertical tables and horizontal forms.
- The vertical form is: assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
- The horizontal row tables are divided into two left and right parts.The left side is the asset bar, and the right side is the liability and shareholder equity column.
The vertical balance sheet is shown below:
The horizontal row balance sheet is shown below

The company usually produces and publishes its balance sheet according to Quaterly, or annual (Annually).When making the balance sheet, in terms of value, the total value of the total amount of assets must be equal to the total value of the total liabilities and the total value of the shareholders’ equity.The calculation formula is as follows:
Asset = liability + shareholder equity
Asset = liability + shareholder ’s equity
For example, when the company receives a $ 50,000 loan from a bank, its assets will increase by $ 50,000, and the liabilities will increase by $ 50,000.If the company receives a investment capital of $ 90,000 from shareholders, the asset increases by $ 90,000, and the shareholders’ equity increases by $ 90,000.
The balance sheet is of great significance for company managers and investors:
- For company managers, when conducting the internal review of the company, the company’s operations can be understood by the company’s operations through different periods of time, so that problems are found in time and the operation plan is adjusted.
- For investors, investors can understand the company’s main resources, how to obtain funds, profitability, and debt equity ratio such as the balance sheet.It is worth investing.At the same time, investors can compare the balance sheet of similar companies to formulate investment strategies.
Of course, the balance sheet also has its deficiencies.The shortcomings of the balance sheet are:
- The balance sheet only shows the information of a certain time point (for example, a certain year, a month, and a certain day), which is a static reflection of the business activities of the enterprise.
- The balance sheet often needs to be used with other financial reports (such as profit statement, cash flow statement, and changes in shareholders’ rights and interests) to specificly understand the real situation of the company’s operations;
- The value on the balance sheet may change the differential depreciation calculation method or the different accounting calculation method, so that the value on the balance sheet cannot completely reflect the actual situation.
What are the components of the balance sheet?
The balance sheet is mainly composed of three parts, namely:
- Assets (asset)
- Liability
- Sharehold ’s equity
1.Asset (asset)
Assets refer to all the assets owned by the company when making the asset liability statement, which mainly include the current assets and the non-current assets.Some tables will use long-long assets instead of nonLouple assets.
The main contents contained in mobile assets and non-fluid assets/long-term assets are::
Moral assets (Current Assets) | |
Accounts Receivable | The part of the company’s income has not been recovered |
Inventory | For companies that manufacture and sell physical products, the finished products, products and raw materials stored in the warehouse |
Cash (CASH) | Including all checks, bank account deposits, etc. |
Cash equivalents | The company can quickly become cash assets, such as government bonds, securities, currency market funds or commercial bills, etc. |
Prepaid expenses (Prepaid Expenses) | The company has paid for business expenses, including insurance, advertising contracts, or rent, etc. |
Marketable Securities | The company holds the ownership or bond certificate of the amount labeled by the ticket surface |
Non-Current Assets / Long-term asset (Long-Term Assets) | |
Tangible Assets | Including LAND, Machine (Machine), Equipment, Building, etc., this part is the company’s tangible fixed assets |
Intangible Assets | Including patents, trademarks, brands (Brands), intellectual property, goodwill, etc. |
2.Liabilities
Liabilities refer to all kinds of contents that should be paid by all loans, debt, wages, taxes, etc.
Liabilities mainly include: Current Liabilities and Noncurrent Liabilities.Similarly, some forms use long-term liabilities instead of non-liabilities.
The main contents of liabilities and non-current liabilities/long-term liabilities are:
Current liabilities (Current Liabilities) | |
Accounts Payable | Including hydropower costs, online rental fees, employee wages, etc. |
Tax liabilities | Various taxes and fees generated during the company’s operation |
Noncurrent Liabilities / Long-term liabilities (Long-Term Liabilities) | |
Loans (Loans) | Loans generated after borrowing loans from banks |
Long-Term DEBT | Including any interest and principal of the issued bonds |
Pension Fund Liability | Refers to the company’s money to pay the employee’s retirement account |
Deferred tax liability | Refers to taxes and fees that may occur due to adjustments and other situations, that is, taxes and fees that should be paid in the future |
3.Shareholder ’s Equity
Shareholders ‘English English is Shareholder’s Equity, sometimes called “owners’ equity”, or “book value”, which refers to deducting all the remaining assets of the company’s arrears.Therefore, shareholders, shareholdersThe calculation formula of equity is as follows:
Shareholder rights = assets – Liability
Depending on the company’s operating methods, there may be Preferred Stock, common stock (Common Stock), and RetAINED EARNENGS.
Sharehold ’s Equity / owner’s equity (Owners’ Equity) | |
Preferred Stock | The company’s income is preferred to assets holding the assets holding the preferred shareholders |
Common Stock (Common Stock) | In the company’s income, the assets assigned to the assets holding ordinary shareholders |
RetainEd Earnings | The company extracts some of the internal savings of the enterprise from past profit. |
How to understand the balance sheet?
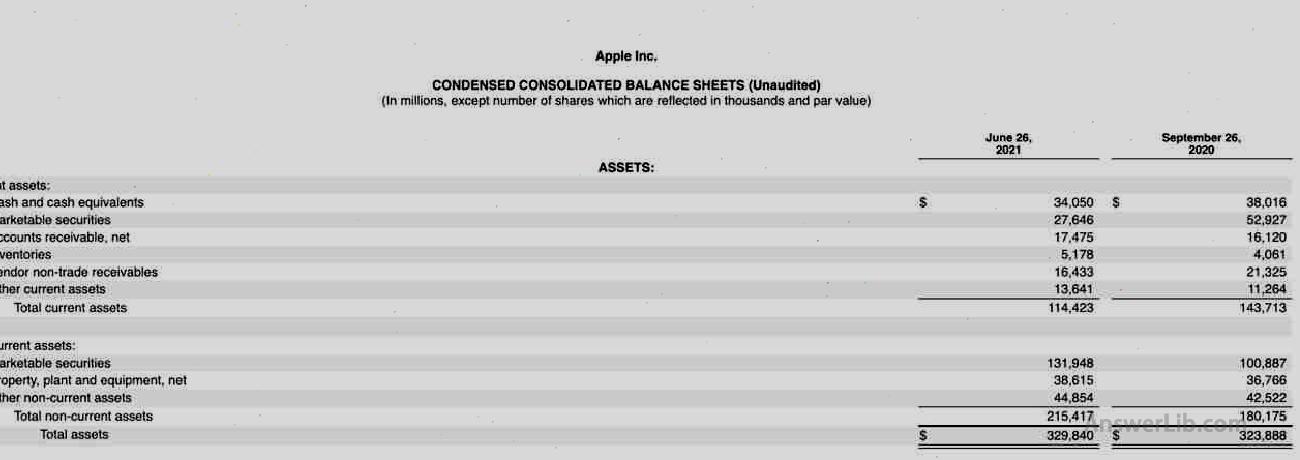
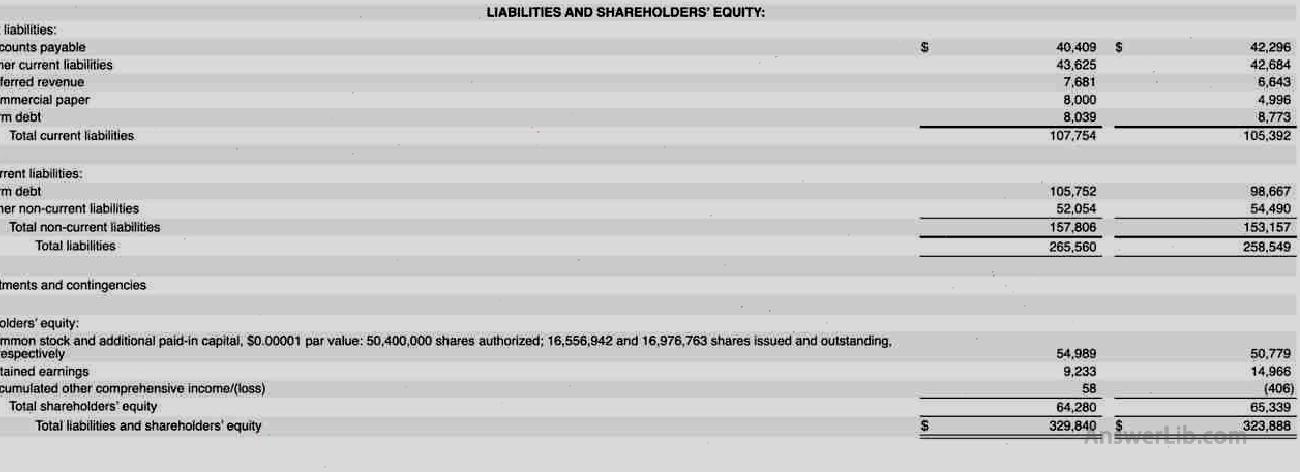
Take the balance sheet released by the Apple from the SEC on June 26, 2021 as an example:

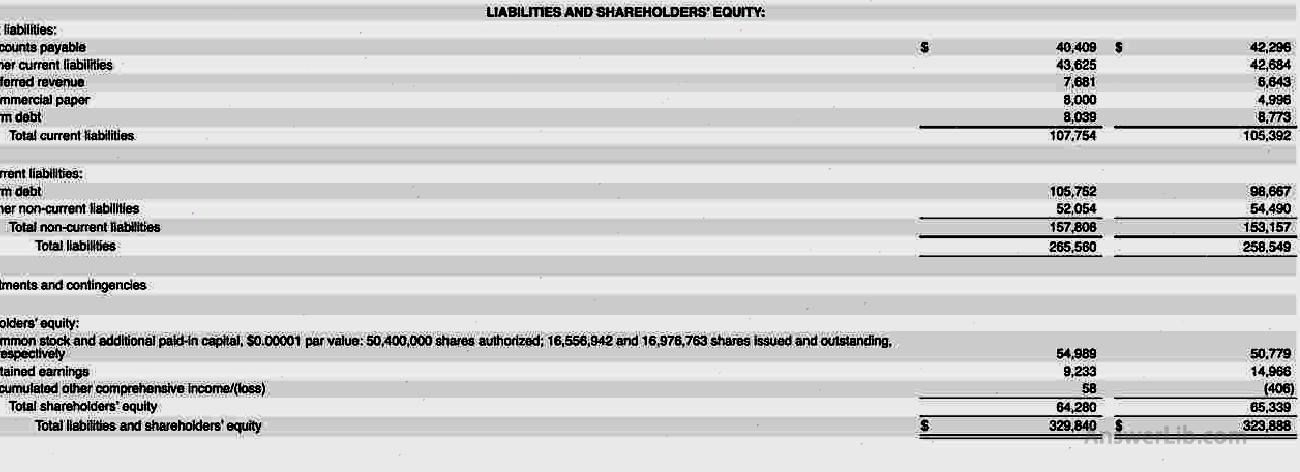
It can be seen from the above Apple’s balance sheet:
- The report date of this balance sheet is June 26, 2021, and the data is compared with data on September 26, 2020.
- The total assets of Apple Inc on the report date are $ 329,840, of which mobile assets are $ 114,423, and non-liquid assets are $ 215,417.
- Compared with September 26, 2020, the total assets of Apple Inc increased by $ 329,840 -$ 323,888 = $ 5,952.
- The total liabilities of Apple Inc on the report date are $ 265,560, of which mobile liabilities are $ 107,754, and non-liquid debt is $ 157,806.
- Compared with September 26, 2020, Apple Inc’s total liabilities increased by $ 265,560- $ 258,549 = $ 7,011.
- Compared with September 26, 2020, Apple Inc’s shareholders’ equity has been reduced by $ 1,059.
- At the same time, the company’s retain income was $ 9,233, a decrease of $ 14,966- $ 9,233 = $ 5,733 compared with September 26, 2020
From the data of the above asset liability statement, it can be judged that during the period from September 26, 2020 to June 26, 2021, Apple Inc’s asset value-added is less than liabilities, and shareholders’ equity and retention income have declined.The specific operational situation needs to be further studied in combination with more other financial statements.
What financial information can I read from the balance sheet?
According to the different data released in the balance sheet, you can also get a number of companies’ financial and development status through different formulas, such as the LIquidity Ratio, Current Ratio, Solvency Ratio, Working Capital, DebT-to-Capital Ratio, and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and And DebT-to-Capital Ratio, and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and and And Debt-to-Capital, DEBT To Equity Ratio, etc.
Assuming, the current balance sheet of Company A is shown below:
| Total assets (ASSETS) | $ 60,000 |
|---|---|
Moral assets (Current Assets) | $ 40,000 ($ 10,000) |
Non-current assets | $ 20,000 |
total liability | $ 40,000 |
|---|---|
| Current liabilities (Current Liabilities) | $ 10,000 |
| Non-current liabilities (NON-CURRENT LIABILITIES) | $ 30,000 |
Shareholder rights (Shareholder ’s Equity) | $ 20,000 |
|---|
1.Liquidity Ratio or Quick Ratio)
The ratio of flow assets, also known as the “liquidity ratio”, English is LIquidity Ratio or Quick Ratio, which is mainly used to measure the level of the company’s operating assets and remove some asset liquidity in the inventory.
Calculation formula | Rapid asset ratio = (mobile asset-inventory) / liabilities Liquidity ratio = (Current Assets – Inventories) / Current Liabilities |
Numerical | The higher the ratio of the rate of liquid assets, it shows that the current stock as the company currently owns is more full and has greater capabilities to cope with possible mobility debt |
Exemplary example | The ratio of flow assets = ($ 40,000 -$ 10,000)/ $ 10,000 = 3.0 |
2.The flow ratio (Current Ratio)
The English ratio English is Current Ratio, which shows that the company’s ability to use mobile assets to repay mobile debt.
Calculation formula | Liquid ratio = mobile assets / liabilities Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities |
Numerical | The higher the mobile ratio, it means that the company’s mobile assets are sufficient and have enough ability to pay the liquidity debt without the need to bear long-term debt |
Exemplary example | The flow ratio = $ 40,000 / $ 10,000 = 4.0 |
3.Working Capital
Operating capital in English is Working Capital, which reflects the difference between mobile assets and liabilities, which represents the company’s ability to perform mobile debt, including paying wages, payment of operating bills and short-term loans, etc.
Calculation formula | Operating capital = flow assets-liabilities Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities |
Numerical | The higher the value, the more capable of the company’s new short-term debt in the operation; if it is negative, it means that the company does not have enough funds to maintain business operations |
Exemplary example | Operating assets = $ 40,000 -$ 10,000 = $ 30,000 |
4.DEBT-TO-CAPITAL RATIO or DEBT-to-Total Assets)
The English liability ratio English is the DebT-TO-Capital Ratio or DebT-to-Total Assets, which shows that all the assets of a company’s current assets are the proportion of assets provided by debt.
Calculation formula | Capital and liability ratio = total liabilities/total assets DEBT-TO-CAPITAL RATIO = Liabilities / Assets |
Numerical | The higher the total amount of debt, the more debt, the more debt companies are carrying, and the less shareholders can obtain the rights |
Exemplary example | Debt occupancy asset ratio = $ 40,000 / $ 60,000 = 0.67 |
5.Debt-to-Equity Ratio
Debt equity ratio, also known as the “debt equity ratio”, English is DebT-to-Equity Ratio, indicating the company’s current shareholders’ equity and debt binding relationship.
Calculation formula | Debt equity ratio = total liabilities / total shareholders’ equity Debt-to-Equity Ratio = liabilities / Shareholders ’s Equity |
Numerical | The higher the value, it means that the higher the debt of the company owned by the equity of the company |
Exemplary example | Equity and liability ratio = $ 40,000 / $ 20,000 = 2 |
What is the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet?
The Federal Reserve’s balance sheet English is Fed Balance Sheet.It is the financial statement published on its official website around 4:30 pm on its official website every Thursday.The content is the analysis of the assets and liabilities held by the Federal Reserve.It summarizes the main factors that affect the supply and absorption of the Fed’s funding.Fed official website Check the current and past asset liabilities.
Similar to the asset-liability statement of ordinary companies, the Fed’s balance sheet is also composed of two parts: assets and liabilities, but there is no shareholder’s equity part.
The assets in the Federal Reserve’s asset liabilities are all Treasurys, government securities, mortgage-based Securites (MBS), and loans provided to banks.Among all types of assets, US Treasury bonds account for 75%to 90%of the share, which is definitely a big head.
The liabilities are all funds held in all the currency in circulation, as well as member banks and US deposit institutions.
In the past, the Fed’s balance sheet did not receive much attention, but after the subprime mortgage crisis from 2007 to 2009, due to the special monetary policy implemented by the Fed during the financial crisis, and the Fed can actively create funds (PrintingDollars’s special authority makes people start paying attention to the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet, and estimates whether the future monetary policy is expanded or tightened.
From the past, the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet can be seen that in August 2007 before the financial crisis broke out, the total amount of the Fed’s balance sheet was about 870 billion US dollars.After the outbreak of the financial crisis in 2008, the Fed began to implement a quantitative easing policy.English is Quantitative Easing, referred to as QE.
The quantitative easing policy is worthwhile that the Fed purchases a large number of government securities or other securities from the market to increase the amount of currency supply and make it beyond the level that it can reach by the normal open market operation to stimulate the market economy.After the implementation of the quantitative easing policy, in January 2015, the total value of the Fed’s balance sheet expanded to $ 4.5 trillion, which was more than five times before the financial crisis in 2008.After that, the market area was stable, and the value of the Fed’s balance sheet also showed a stable trend.
Professionals in the industry believe that the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet can help analysts understand the scope and scale and duration of the Fed’s participation in market operations.When the total value of the balance sheet increases the market economy, it is mainly responsible for stabilizing the economic situation when shrinking.
How to understand the Fed’s balance sheet?
The Fed has demolished its balance sheet into seven forms to report its assets and liabilities in detail.The most important asset-liability information can be obtained from Table 5, and Table 5 is more direct and clear.The current Fed’s asset debt situation.
Table one | List the factors that affect the balance of the deposit institution (Reserve), in detail the factors of the supply and absorption reserve balance, and the level of the current reserve balance | 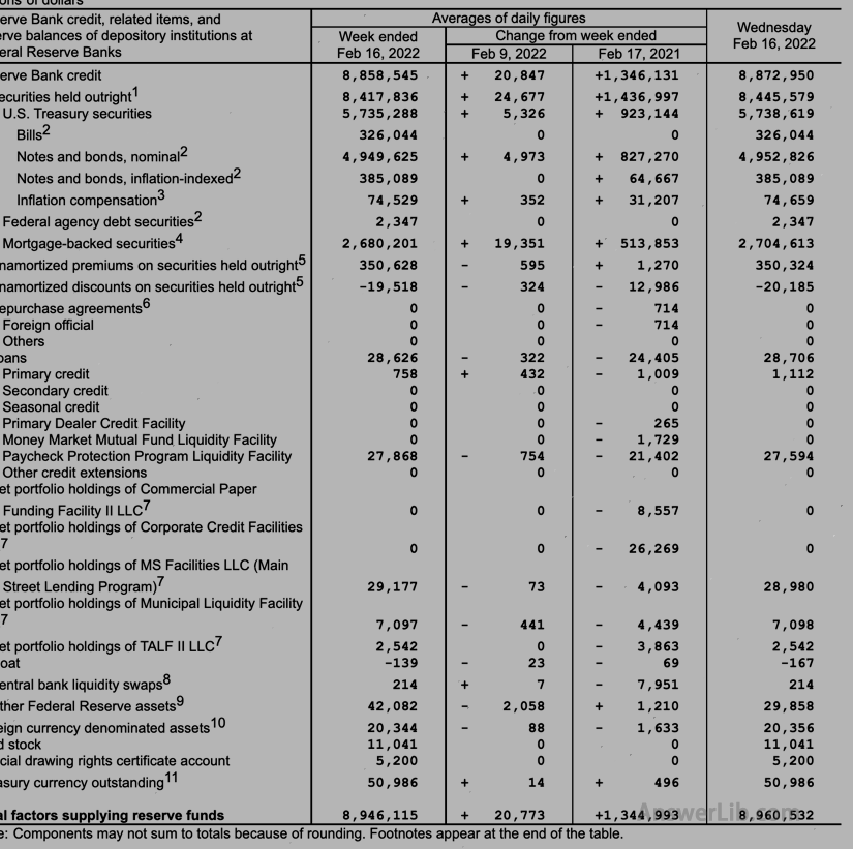 |
Table 2 | List the Federal Reserve’s current securities, loans and some other assets, as well as the terminal distribution of liabilities | 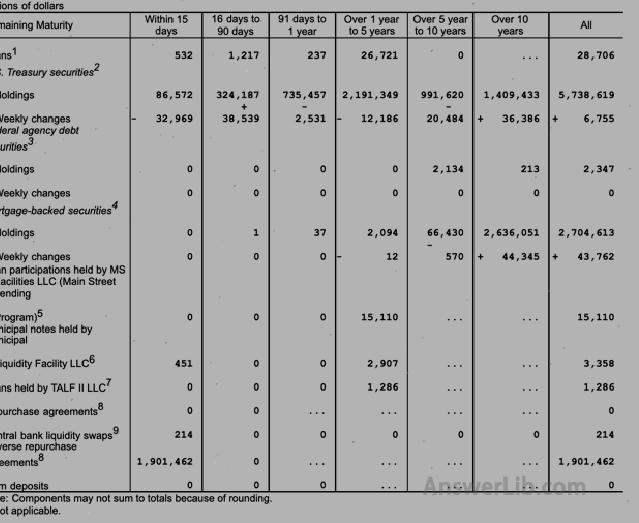 |
Table three | Supplementary information of mortgage-back securit |  |
Form 4 | The content covers information about the amount of non-repayment loan principal provided by the Reserve Bank to the limited liability company.The information about Credit Facilities Limited Liability Companies (LLCS), including the purchase amount of unpaid facilities assets and the state treasuryDonation and other assets | 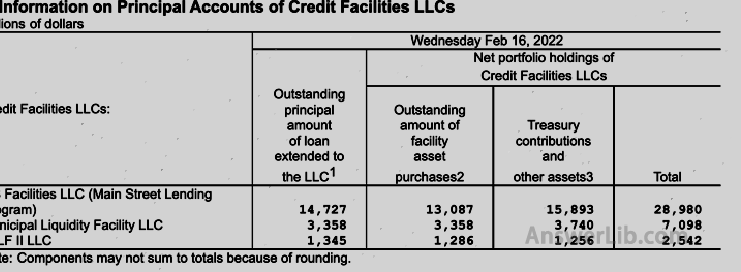 |
Table 5 | Table 5 is the balance sheet of the Federal Reserve system: The first page shows the assets held by the Federal Reserve The second page shows the debt of the Federal Reserve | 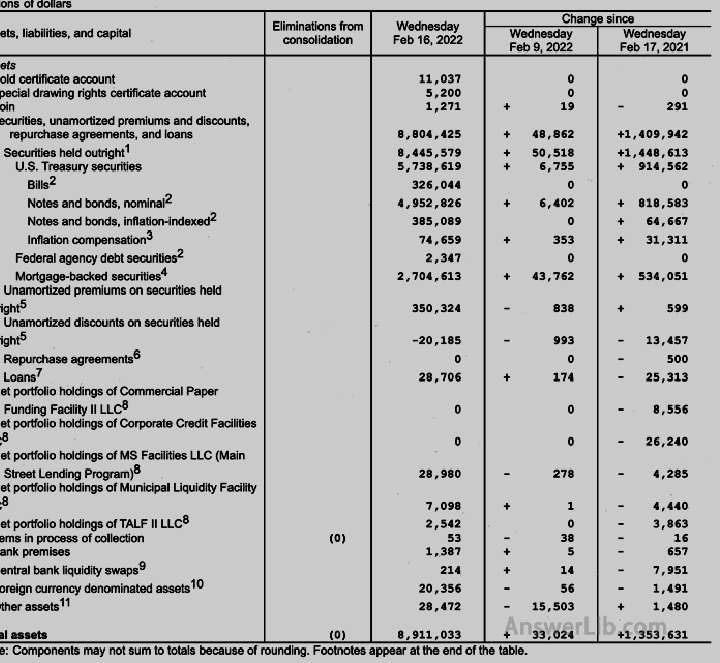 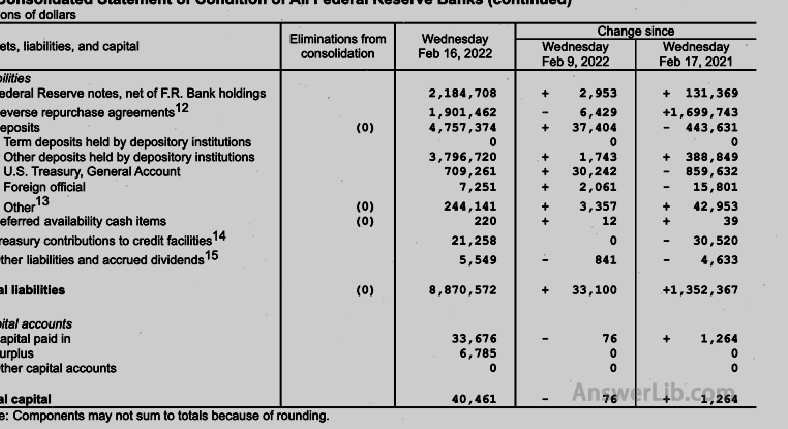 |
Table 6 | Provided data from each federal reserve bank | 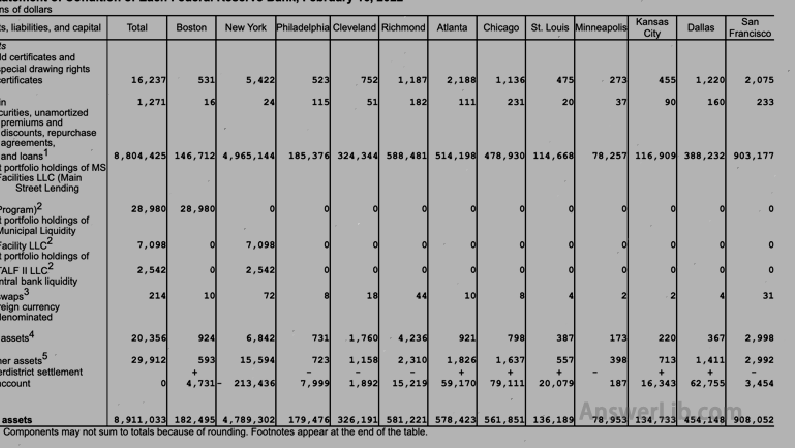 |
Table Seven | Provide information about assets for the Federal Reserve bill mortgage | 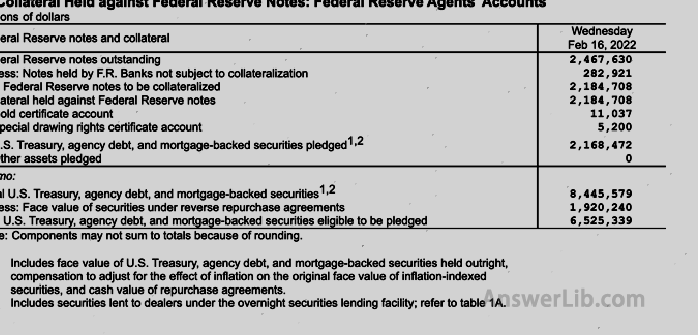 |
Fed’s asset-liability trend chart
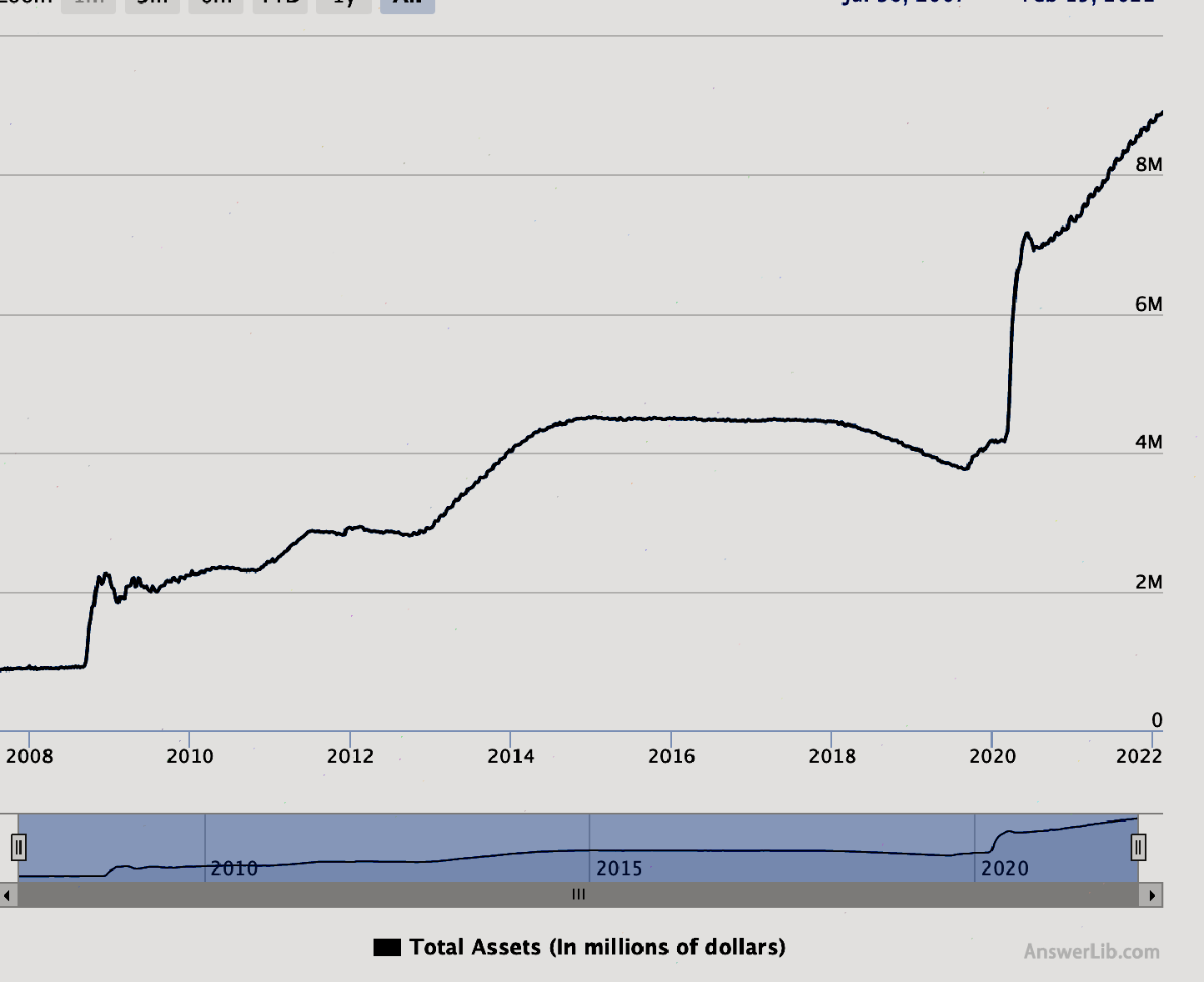
It can be seen from the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet in 2022 that after a substantial growth in the financial crisis period from 2007 to 2009, the total value of the balance sheet has entered a relatively stable growth stage, and then it is a stable stage.The total value is 4.5 trillion yuanAbout US dollars.After that, it contracted to about 3.78 trillion US dollars to stabilize the US economy at the time.
However, in 2020, due to the large explosion of COVID-19, the economic situation was severely impacted, and the Federal Reserve intervened again.The total value of the balance sheet rose sharply again, rising to about $ 7 trillion in 2021, and continued to increase to 2022 to 2022In the year, it was close to 9 trillion US dollars.Although the economic situation stabilized, the price of the stock market and the housing market was extremely high, and at the same time, it caused a large inflation (the inflation rate in January 2022 reached a 40 -year history of 40 years.7%), thus forming a larger economic bubble.
American Langshang Daquan
American brokerage ranking and comparison [2024] Recommended by the 12th National American brokerage firms
More company valuation
- Julian Roberts – Julian Robertson: Father of Tiger Baby
- Explore the 24 first-level dealers of the Federal Reserve
- Important Finance and Investment News
- What is a corporate value multiple?Enterprise Multiple
- What is preferred stock?Preferred stock
- What is the operating leverage coefficient?Degree of Operating Leverage
- What is debt repayment payment rate?DEBT Service Coverage Ratio
- What is capital expenditure?Capital Expendital
- What is the capital asset pricing model?Capital Asset Pricing Model
- What is financial leverage coefficient? Degree of Financial Leverage
