Operating leverage coefficient, English is DEGREE of Operating Leverage, referred to as DOL, also known as “operating leverage”.profit The degree of influence of change.When calculating the operating leverage coefficient, use a specific financial cycle EBIT The change rate and sales rate of sales can get the company’s operating leverage coefficient in the financial cycle.
The degree of operating leverage marks the correlation between the company’s profit change and sales changes.The higher the DOL value, it means that when the company’s sales increase, its profits will rise sharply.Profit profits will also be greatly reduced.When the DOL value is low, the impact of changes in sales on the high and low impact on profit and return will be less.At the same time, because the company’s profit involves the relationship between sales and fixed costs and variable costs, it can also be used to evaluate the company’s operating costs, the proportion of fixed costs.
In addition to evaluating the company’s own cost model and operating model, the level of the DOL value will also have a certain impact on the company’s stock price volatility, because investors will make investment reactions by checking the company’s income report.
Bleak American broker:Transparent securities| | Futu Securities| | Microex Securities| | Tiger securities| | First securities| | Robinhood in| | American Langshang Daquan
Directory of this article
- How to calculate the operating leverage coefficient?
- How to calculate Apple’s operating leverage coefficient?
- What is the significance of the investment leverage coefficient?
- What are the limitations of operating leverage coefficients?
- Join investment discussion group
- More US stock investment strategies
How to calculate the operating leverage coefficient?
The basic calculation formula for operating leverage coefficients is to remove the company’s pre-interest rate change in interest taxation and sales of the company during the financial year, that is,:
Business leverage coefficient = profit change rate before interest tax / sales change rate
DOL = %& Nbsp; Change & Nbsp; in & Nbsp; EBIT / %& Nbsp; Change & Nbsp; in & Nbsp; Sales
in:
EBIT The calculation method is to add the company’s interest expenses and tax expenses to the company’s net income, that is,
Before interest taxation & nbsp; = & nbsp; net income & nbsp;+& nbsp; interest & nbsp;+& nbsp; taxation
Ebit = net intertome + interest + taxes
The change of profitability before interest taxation is to reduce the EBIT value at the beginning of the period at the end of the financial year, and then divide the EBIT value at the beginning of the period, that is,:
The change rate of profit before interest tax = (EBIT value at the end of the period-early EBIT value) / EBIT value at the beginning of the period
The calculation method of the change of sales is to reduce the sales at the end of the financial year off the sales of the initial sales at the beginning of the period, and then divide the sales at the beginning of the period, that is,:
The change rate of sales = (final sales-initial sales) / Time-to -date sales
In addition to the above formula, the change rate of operating income and sales can be removed, that is::
Business leverage coefficient = change rate of operating income / sales change rate
DOL = %& Nbsp; Change & Nbsp; in & Nbsp; Operating Income / %& Nbsp; Change & Nbsp; in Sales
in:
Operating income is the total income value of the financial year minus operating expenses, that is:
Business income = total income-operating expenses
Operating infy = gross income -Operating expenses
The calculation method of operating income change is the same as above.
The difference between the two calculation methods is the profit value used::
- The first way is used EBIT(EBIT) This part includes income and costs outside business activities.Considering debt interest and tax payments, you can consider the company’s profits in operations more completely;
- The second method excludes off-business income and expenses, and can evaluate the relationship between profits and sales more for the company’s core business during use.
There are two variants for the calculation of the operating leverage coefficient:
The first: eliminate marginal income with operating income, that is,:
Business leverage coefficient = marginal income / camps, income
Dol = C ONTRIBUTION Margin / Operating Income
The second: use marginal income and the difference between marginal income and fixed costs, that is:
Business leverage coefficient = marginal income / (marginal income-fixed cost)
DOL = Contribution Margin / (Contribution Margin – Fixed Costs)
in:
CONTRIBUTION Margin It is to reduce the company’s sales revenue to a variable cost.After paying fixed costs, the remaining income can be regarded as the company’s income.The calculation method is:
Edge income = sales-variable cost
Contribution Margin = Sales – Variable Costs
- Variable Costs refers to the cost of a proportional relationship between the company in the production and sales of the company, such as raw materials, packaging costs, or retail companies’ credit card transactions, transportation fees, etc.
- Fixed Costs refers to the cost of cost that does not change with the changes in the company’s sales.It is the cost that the company must pay no matter how its sales capabilities, such as the rent of the plant.
From the variant formula of DOL, the relationship between the DOL value and the fixed cost, that is, the higher the fixed cost, the higher the DOL value, the higher the correlation between the change of the company’s operating profit and the change of sales.
how Calculate Apple’s operating leverage coefficient?
10-k released by Apple in September 2021 Financial report Calculate the instance:
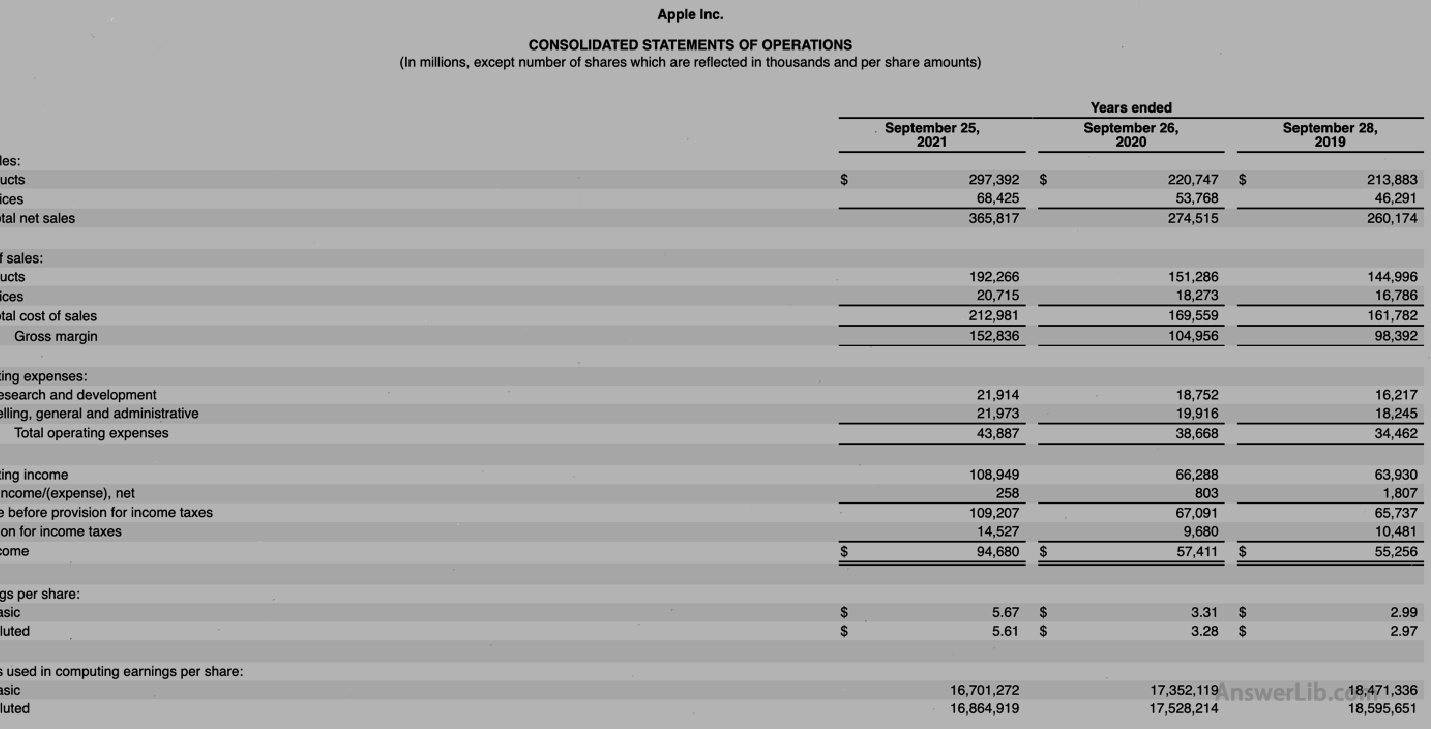
AAPL Financial Report middle Profits The data tables such as other income and expenditures are shown below:
Profit table:
Other expenditures:
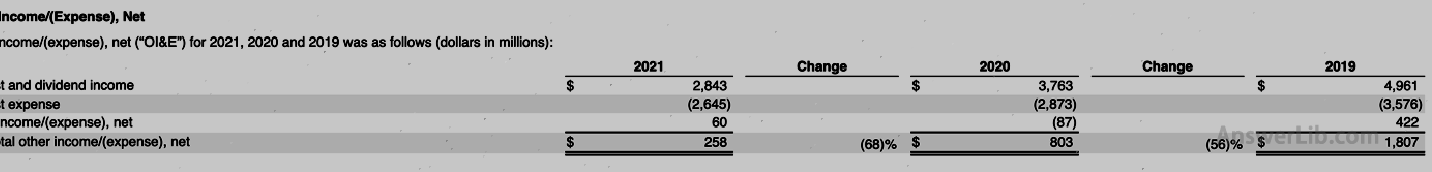
You can see from the data table:
| 2021 | 2020 | |
|---|---|---|
Net income Net income | $ 94,680 m | $ 57,411 m |
Tax expenditure Income taxes | $ 14,527 m | $ 9,680 m |
Interest expenditure Interest | $ 2,645 m | $ 2,873 m |
Ebitit | $ 111,852 m | $ 69,964 m |
Sales Sales | $ 365,817 m | $ 274,515 m |
Operating income Operating infome | $ 108,949 m | $ 66,288 m |
so:
EBIT change rate = ($ 111,852 m – $ 69,964 m) / $ 69,964 m = 59.87%
The change rate of sales = ($ 365,817 m – $ 274,515 m) / $ 274,515 m = 33.26%
The change rate of operating income = ($ 108,949 m – $ 66,288 m) / $ 66,288 m = 64.36%
Calculate using formula:
Business leverage coefficient = profit change rate before interest tax / sales change rate
DOL = %& Nbsp; Change & Nbsp; in & Nbsp; EBIT / %& Nbsp; Change & Nbsp; in & Nbsp; Sales
= 59.87% / 33.26%
= 1.80
Use formula 2 calculation:
Business leverage coefficient = change rate of operating income / sales change rate
DOL = %& Nbsp; Change & Nbsp; in & Nbsp; Operating Income / %& Nbsp; Change & Nbsp; in & Nbsp; Sales
= 64.36% / 33.26%
= 1.94
As can be seen from the results of the formula 1, it can be seen that in the 2021 financial year of Apple, the sales of sales will change by 1.8%in the same direction, that is, the sales of sales increased by 1%, and the profit before interest tax increased by 1.8%increased by 1.8%.Essence
As can be seen from the calculation results of Formula 2, every time the sales increase or decreased by 1%, operating income increased or decreased by 1.94%.
What is the significance of the investment leverage coefficient?
The main guidance significance of the operating leverage coefficient is to evaluate the relationship between the company’s profits and sales increase and slowing down and slowing down.
- When the operating leverage coefficient is high, the company’s profit increase and decrease of slowdowning and decrease in sales are greatly affected.When the company’s sales fluctuate, the company’s profits will fluctuate more.
- When the operating leverage coefficient is low, the company’s sales are floating, the impact on profits is less.
Another role of operating leverage coefficient is to evaluate the proportion of fixed costs in the company’s cost.
The cost of the company can usually be divided into fixed costs and variable costs.It can be transformed to increase or decrease with the increase or decrease of sales.Thereforecost.Therefore, when the company’s fixed cost is high in total cost, the floating of the company’s sales will have a great impact on the floating profit.
In other words, if a company has a high operating leverage coefficient, it can be considered that the cost of this company is relatively high.
For investors, the operating leverage coefficient is also a role that can be used to estimate the size of the company’s stock volatility.When the company’s operating leverage coefficients are high, it means that the company’s profits and sales have a more sensitive influence relationship, and profits are financial indicators that investors will directly refer to when investing in the company.If the coefficient is high, the company’s profit volatility is relatively large, and unstable profits will make investors’ investment attitude towards the company’s investment, which will also be reflected in the large volatility of the stock price.
What are the limitations of operating leverage coefficients?
When using the operating leverage coefficient, the company’s different income and assets have not been carefully analyzed, so it is difficult to make a relatively comprehensive financial assessment of the company’s operating conditions.
At the same time, this value does not use the value of shareholders ‘equity, so it cannot obtain the influence between shareholders’ equity and company operations from the values.
Therefore, if investors want to get more effective investment guidance, more financial indicators other than this ratio need to be combined to conduct comprehensive analysis.
Join investment discussion group
Publish the latest market information on a regular basis and share your investment experience:
