Book value English is Book Value, which is often called “Shareholder’s Equity”, which is an indicator to measure a company’s net asset.
The book value can not only evaluate the net assets of listed companies, but also measure the net assets of unlisted companies.The company’s book value is calculated based on the difference between the total assets provided in the balance sheet issued by the company and the total debt provided by the company, so the book value is like its name.Real asset value embodies.
It should be noted that there is also an Intangile Book Value, which calculates the difference between tangible assets and total liabilities.Among the tangible book value, it does not include intangible assets held by the company, such as patented technology, intellectual property rights, etc.Therefore, in actual use, for example, when the company is liquidated, it can better evaluate the company’s actual net assets.
Investors often use the book value of the company to compare with the company’s market value.Combine the number of circulating shares to calculate the book value per share, Net rate Wait, the analysis of these combination data measures whether the stock price of a listed company is overestimated or underestimated.
Book value per share English is Book Value Per Share, also known as “net stock” or “net assets per share”.It is a net asset value of listed companies on the basis of each share.The calculation method of the book value per share is to compare the company’s book value compared with all the number of circulating shares.
Investors usually calculate the company’s book value per share, and then compare it with the company’s current market price to measure whether the company’s stock price is underestimated.The company’s stock is more valuable and the price should rise.
Bleak American broker:Ying Diandai 劵| | Futu Moomoo| | Microex Securities| | Tiger securities| | First securities| | Robinhood in
Directory of this article
- How to calculate the book value?
- How to calculate the book value per share?
- Child value calculation example
- Each account value calculation example
- What is the significance of investment in book value?
- What are the limitations of book value?
- The difference between book value and market value
- More company valuation
How to calculate the book value?
The calculation method of book value is to minus the total assets in the company’s financial report off the total liabilities, that is,:
Book value = total assets-total liabilities-preferred shares
Book value = Total Assets – Total Liabilities – Preferred Stock
Among them, total assets and total liabilities can be found in the company’s Balaance Sheets.
For tangible book value:
Topo account value = book value-intangible assets
Tangible Book Value = Book Value-intangible Assets
The above tangible assets can be in Balance sheet Find in Balance Sheets.
How to calculate the book value per share?
The calculation method of the book value per share is to subtract the total assets in the company’s financial report to reduce total liabilities and preferred shares, and then remove the current number of circulating shares, that is,
Book value per share = (total asset-total liabilities-preferred shares) / number of circulation shares
BOOK VALUE PER ShaRE = (Total Assets – Total Liabilities – Preferred Stock) / Shares Outstanding
For tangible book book value per share, the value of tangible book value is eliminated with the number of circulating shares, that is:
Tangible book value per share = (book value-intangible assets) / number of circulation shares
Tangible Book Value Per Share = (BOOK VALUE-intangible Assets) / Shares Outstanding
Among them, total assets and total liabilities can 10-K financial report Find in.
Child value calculation example
This chapter will be released by Apple in September 2021 10-K financial report Calculate the instance:
AAPL Financial Report The balance sheet in the middle is shown below:

It can be seen from the balance sheet that the total assets of Apple in the 2021 financial year are $ 351,002 m, and the total liabilities are $ 287,912 m, so its book value is:
BOOK VALUE = Assets – Liabilities
= $ 351,002 m – $ 287,912 m
= $ 63,090 m
Therefore, the book value of Apple based on the 2021 financial year is $ 63,090 m.
At the same time, there are tangible book value = book value-intangible assets.For AAPL, in the balance sheet, there is no direct display of intangible assets, so it has tangible book value = book value.
Each account value calculation example
This chapter will be released by Apple in September 2021 10-K financial report Calculate the instance:
AAPL Financial Report The comprehensive business reports are shown below:
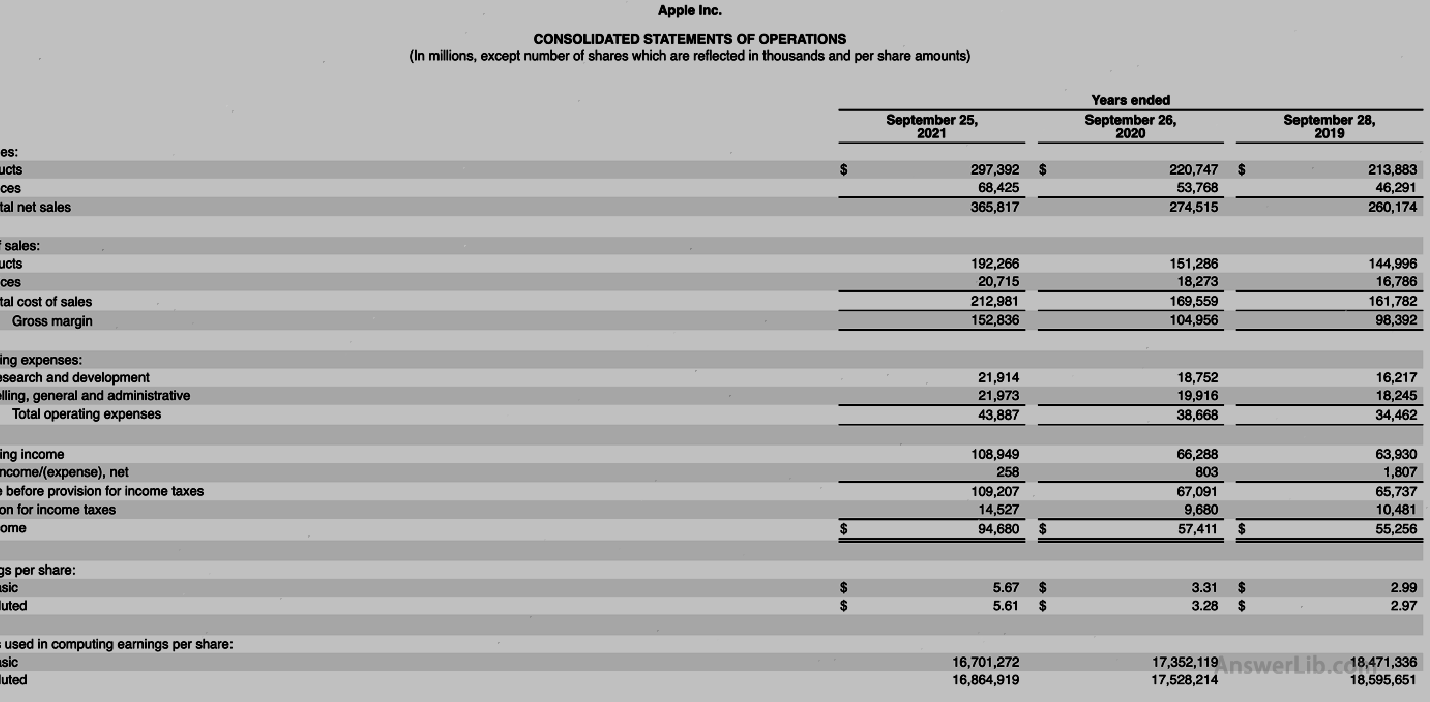
From the data table, we can know that Apple’s circulation shares are (16,701,272 x 1000) shares.
From the previous chapter, it is known that Apple’s book value and tangible book value are equal, and it is $ 63,090 m.Therefore, Apple’s tangible book value per share in the 2021 financial year is equal to the book value per share, that is::
Tangible book value per share = each share value = book value / number of circulation stocks
= $ 63,090 m / (16,701,272 x 1000)
= $ 3.78
What is the significance of investment in book value?
- The book value is usually compared with the company’s market value.The company’s market value (Market CAP) is to multiply the company’s current stock price with the number of circulating shares.Generally speaking, when the company’s book value is greater than the market value, it will think that the company’s stock price is affected.Undergraduate, most investors are more willing to study stock value of these book value than market value.On the contrary, if the book value is less than the market value, it may be considered to be overestimated by the company’s stock.
- Investors often combine the book value with other financial data and analyze the company’s operating capabilities in depth, mainly to combine the number of accounts per share with the number of circulating shares, and compare the price per share to the price per share.To analyze that the company’s stock is overestimated or underestimated.
- The book value per share (BOOK VALUE PER ShaRE, referred to as BVPS), removes the company’s book value with the current number of circulating shares.The benefits that ordinary shareholders can get, which is one of the values that investors are more concerned.
- The PRICE-TO-BOOK RATIO (P/B RATIO) is compared with the company’s price per share.When the market net ratio is greater than 1, it meansThe account value of the stock will think that the stock is overvalued.On the contrary, if the company’s value per share is lower than the book value per share, it may be considered to be underestimated.
- Another use of book value is to measure the net assets of a company that has not yet been listed.Because these companies have not yet listed, they cannot obtain their market value, but they can measure their book value through the actual assets of the company.When the company is listed, when the company is listedInvestors can judge the company’s development progress based on the company’s book value and market value changes.
What are the limitations of book value?
Another use limit for book value is that if the development of a company is measured through historical book value, when a company with a large amount of assets sells its assets in large quantities, its book value will fluctuate largeIn the fluctuations, it is impossible to clearly analyze what the company’s operating capacity has changed.
The difference between book value and market value
The company’s market value is multiplied with the current stock price of the company with the current number of stocks in the market.It has high volatility in terms of value.At the same time, it is mainly affected by market sentiment and investor concept.
The company’s book value is to reduce the total debt in the company’s financial statements.The data is provided by the company, which is based on the company’s own operating capabilities, so it is mainly affected by the company’s own profitability.
The difference between the two is:
| Book value Book value | Market value Market Cap | |
|---|---|---|
Calculation | Total assets in financial statements minus total liabilities | The current stock price of the company is multiplied by the current circulation stock |
Influential factors | Mainly affected by the company’s operating capabilities | It is greatly affected by the market |
Can provide company types | Suitable for listed companies, or unlisted companies | Applicable to listed companies |
Value | There may be negative value, zero, positive value | Can’t have negative values |
Some investors will use the company’s book value and market value at the same time to measure the investment value of a company, if at a certain moment:
- Book value is greater than market value: When this happens, it usually indicates that the market temporarily loses its investment confidence in the company, causing a serious decline in the stock price, which may be due to public business problems, litigation losses, and other events that affect investor confidence.But it may also show that this stock is underestimated.
- Book value is less than the market value: When the company is listed, in conventional situations, investors hope that the company’s profitability will perform well, so the stock market will give most companies a higher value.In this case, it shows that the company is in a benign development.The profitability is better than its assets, while having a good ability to expand and increase profits.But it may also show that this stock is overvalued.
- Book value is equal to the market value: When this happens, it shows that the market believes that the company’s current investment value is equal to its assets, so it has a relative valuation.
More company valuation
- Julian Roberts – Julian Robertson: Father of Tiger Baby
- Explore the 24 first-level dealers of the Federal Reserve
- Important Finance and Investment News
- What is a corporate value multiple?Enterprise Multiple
- What is preferred stock?Preferred stock
- What is the operating leverage coefficient?Degree of Operating Leverage
- What is debt repayment payment rate?DEBT Service Coverage Ratio
- What is capital expenditure?Capital Expendital
- What is the capital asset pricing model?Capital Asset Pricing Model
- What is financial leverage coefficient? Degree of Financial Leverage
