Cash flow confusion It is a financial evaluation method based on the concept of currency time value.The basic principle is: in industries that involve cash flow involving cash flow in investment, deposit or company developmentThis will evaluate the future development trend of the enterprise, or the possibility of the current investment in the future may be able to benefit.value investment The love of the person.
In actual use, the appraisers are required to have a more accurate judgment on the enterprise, and then decide the appropriate discount rate to calculate the relatively more accurate cash flow cash folding value.How to calculate the specific cash flow?How to use it?After reading this article, you will understand:
Bleak American broker:Transparent securities| | Futu Securities| | Microex Securities| | Tiger securities| | First securities| | Robinhood in| | American Langshang Daquan
Directory of this article
- What is cash flow?
- How to calculate the cash flow discount “DCF”?
- What is the company’s intrinsic value?
- How to use the cash flow discount current method to calculate the internal value of the company’s stock?
- How to use the cash flow discount current law to calculate the inherent value of US Treasury bonds?Determine whether it is worth investing?
- How to use the cash flow method to calculate dividend investment?
- What are the advantages of cash flow discount?
- What are the disadvantages of the cash flow discount?
What is cash flow?
The cash flow is discounted, and the full name is Discountd CF Cash Flow, referred to as DCF, which is often used to evaluate the inherent value of listed companies (Intrinsic Value).
Cash flow is discounted, using the concept of Time Value of Money to evaluate the inherent value of an enterprise, a stock, or a project, determine whether it is worth investing, or whether your own investment strategy is appropriate.
In terms of basic concepts, cash flow can be simply understood as that the future cash flow is calculated into a specific formula as the current value.The influence of various factors increased, but the increase in this amount cannot accurately reflect the inherent value of the company.For example, due to inflation, the current $ 100 may become $ 120 after 2 years.People will think that the next $ 120 is actually equal to the current $ 100, and the inherent value of this $ 100 will not increase.
Cash flow is usually used:
- Companies with relatively stable cash flow: When a company has a relatively stable cash flow, investors usually have more likely to master the company’s operating capabilities, so that cash flow can be used to obtain a good reference value indicator.
- Companies with multiple sources of income: When a company has a variety of sources of income, using different financial assessment indicators may get a large value, and it is difficult to find a company similar to it, so you can consider using cash to use cash.Folding is now for evaluation.
- Value investors evaluate: When evaluating the company, value investors are more inclined to analyze the company’s financial performance.At this time, using cash flow can be considered well considering the company’s financial capabilities.
- Evaluate banks and real estate companies: Some professionals in the financial industry have found that for banking companies, using cash flow can better determine the value of private equity, and it also has a good evaluation function for real estate companies.
Cash flow is usually not used:
- Companies with cyclical fluctuations in cash flow: For companies with cyclical fluctuations in cash flow, such as house construction companies, because cash flow has significantly changed with the overall business environment, it is difficult to accurately use cash flow to accurately.Evaluate the income.
- Private company: Because it is difficult to obtain the required financial data from private companies, it is difficult to use cash flow to evaluate the company’s cash flow earning ability
- Start-ups or companies that are developing early: For these two types of companies, because there is no sufficient past cash flow data, it is difficult to predict future cash flow.
How to calculate the cash flow discount “DCF”?
The calculation formula of cash flow is:
DCFN= FCF (1+g)1/ (1+r)1+ FCF (1+ G)2/ (1+r)2+ FCF (1+ G)3/ (1+r)3+…+FCF (1+G)N/ (1+r)N
Among them, the FCF was that year Free cash flow(Free Cash Flow), G is Growth Rate, so FCF (1+P)NIt means that the cash flow value of the N-year year can estimate the future cash flow value based on the company’s previous cash flow growth rate.
R is a discount rate.English is Discount Rate.It is a ratio of future expected returns into current value.It usually consists of risk-free interest rates, risk compensation and inflation, that is, R = risk-free interest rate + risk compensation + inflation.The discount rate is one of the most important values when calculating cash flow and is one of the biggest values that affects the biggest value because it has certain subjectivity.
The discount rate is usually composed of risk-free interest rates, risk compensation and inflation.
- Risk-free interest rates usually refer to a fixed rate of return provided by enterprises, banks or stocks, such as bank deposit interest rates, etc.;
- Risk compensation is a ratio set for investors based on investment risk;
- Inflation is a cash flow appreciation that appears in the entire society;
Among the three, risk-free interest rates can usually get a relatively unified value in the previous development of investment objects, but risk compensation has certain subjectivity, while inflation is unknown.As a result, the cash flow calculation has certain limitations in actual use.
for example:
Suppose a company with a stable cash flow growth model A grows at a rate of 5%each year.Last year, the company’s cash flow was $ 2,000,000.If investors hold 10%of the shares, they can get $ 200,000 this year.The company’s understanding is 15%.
So in the next few years, the income that investors can get the year
CFC (1+G)1: $ 200,000 * (1+5%) = $ 210,000
CFC (1+G)2: $ 20,000 * (1+5%) = $ 220,500
CFC (1+G)3: $ 220,500 * (1+5%) = $ 231,525
That is, three years later, investors can get a cash flow of $ 662,025;
Then use the cash flow discount calculation formula:
DCFN= Cf (1+g)1/ (1+r)1+ CF (1+ G)2/ (1+r)2+ CF (1+ G)3/ (1+r)3
= $ 210,000 / (1+15%)+$ 220,500 / (1+15%)2+ $ 231,525 / (1+ 15%)3
= $ 501,568
In general, the cash flow discount current method is an important valuation method for investors to evaluate the inherent value of listed companies or other financial investment products.Let ’s introduce it to what is the company’s inherent value.
When using the cash flow method to calculate the inherent value of the company, in addition to considering the cash flow that the company can bring in the future, the company’s final value must be considered, that is, the company can sell the company in the future.
What is the company’s intrinsic value?
The company’s inherent value, English is the Intrinsic Value.It is based on the value of the company, stock, or any financial products that can generate cash flow.Therefore, the future cash flow needs to be discounted to the present to compare its actual increase in value.If the future cash flow is calculated, it is greater than the current amount of investment, it means that this investment is worth the development, otherwise, this investment may lose value over time.
The company’s internal value = the company’s cash flow cash flow to the present value of the company’s predicted period + the discount value of the company’s final value
The final value, English is the Terminal Value, referred to as TV, refers to the value of assets, business or projects outside the forecast period of estimated future or cash flow.Generally, when the final value is calculated, it will assume that the company will always use the forecast period to always use it forever with the forecast period.Set the growth rate of growth.
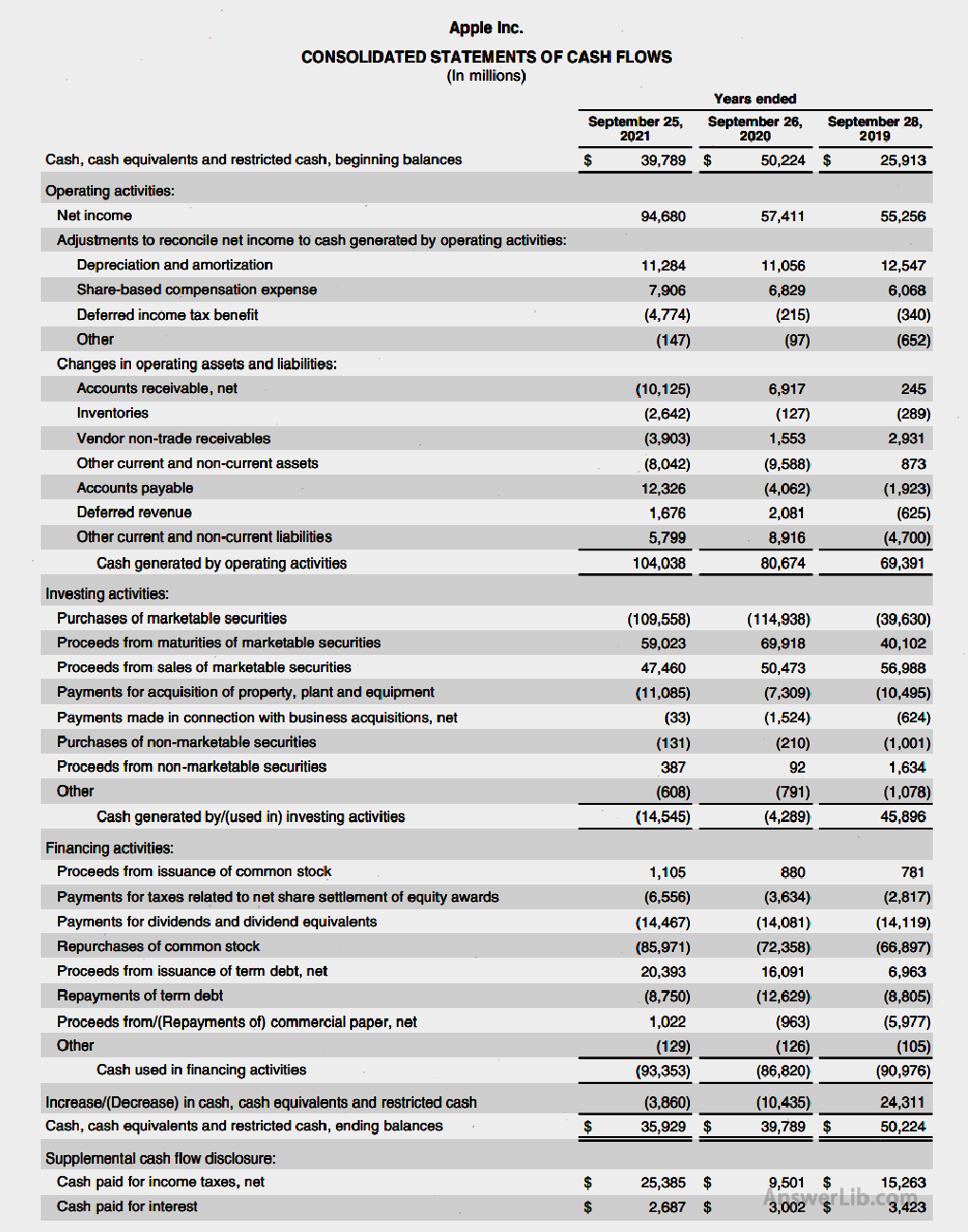
For example, when judging whether the current company’s stock price is worth buying, investors can judge the income they may get through the future cash flow of the company.Determine a predicted discount rate R and a final value discount rate G, calculate the cash flow discount and final value discount value of the predicted period according to the discount rate.They can get the DCF value.Amount B, if B> A, think that this stock is worth buying.If B The amount B the income that may be obtained in the future is calculated through the cash flow discount. Buffett mentioned “what is the inherent value of the company” and “how to use the inherent value of the company to guide investment” on many occasions.Buffett began to use this concept in 1950 and promoted extensively, but before he, Benjamin Graham and David Dodd of Columbia Business School had been trying to use the inherent value and DCF model of calculation companies in the 1920s of the 2020s.Analyze the company’s investment value and make value investment. In this chapter, we will use the cash flow current law to calculate the company’s inherent value, and then compare the company’s inherent value with the current company’s market value: So what is the company’s market value? The company’s market value, English is the Market Capitalization, referred to as Market Cap, indicating that the total value of all the stocks issued by the company currently issued.The calculation method is as follows: Market Cap = Price Per Share x Shares Outstanding Market value = US stock price X circulation stock number Among them, Price Per Share is the stock price and is updated daily; the number of circulating shares can be obtained from the company’s quarterly financial report or annual financial report. Free Cash Flow (FCF) refers to the free cash flow that shareholders can obtain and distribute.For companies that issue stocks, the free cash flow that can be assigned to shareholders is:: Free Cash Flow = Earnings Before Interest and Taxes / EBIT + depreciation and amortization -Taxes -Changes in WORKING Capital — Capital This expenditure (Capital Expendital / Capex) Among them, pre-interest taxation profits, depreciation and amortization, and taxation can be found in the company’s gains and losses, and operating capital and capital expenditure can be Balance sheet Find in. Calculate the cash flow of free cash flow at present.Use the same formula.Assume that the company’s free cash flow will grow at a ratio of G each year: DCFN= FCF/ (1+r)1+FCF (1+G) / (1+R)2+ FCF (1+ G)2/ (1+r)3+…+FCF (1+G)(N-1)/ (1+r)N When using free cash flow, because of removing cash flow that most shareholders cannot share, it can more accurately reflect the ability of shareholders to earn cash flow from investment. Take Apple as an example, Through its own cash flow calculation formula, the free cash flow of Apple 2021 Financial Year is: Free Cash Flow = Cash Generated by Activities -Payments for Acquisition of Property, Plant and equipment = $ 104,038M – $ 11,085M = $ 92,953M = $ 92.95B Therefore, the above is the free cash flow of that year.The next step can predict the free cash flow in the next few years. The growth rate of the company is to calculate the company’s free cash flow in the next ten years.There are many prediction methods, which can make the company’s growth rates in the past ten years. September 2021 $ 9.3B 27.4% September 2020 $ 7.3B 23.7% September 2019 $ 5.9B -7.8% September 2018 $ 6.4B 23.1% September 2017 $ 5.2B The average growth rate in the past 5 years is: 16.6% Through the analysis of the growth of the company’s previous cash flow, set a reasonable proportion of cash flow growth.Take Apple as an example.In September 2021, Apple’s cash flow was $ 9.3B.Apple’s cash flow in the next 10 years is: September 2021 “Current” $ 9.3B September 2022 $ 9.3b x (1+16.6%)1= $ 10.8B September 2023 $ 9.3b x (1+16.6%)2= $ 12.6B September 2024 $ 9.3b x (1+16.6%)3= $ 14.7B September 2025 $ 9.3b x (1+16.6%)4= $ 17.2B September 2026 $ 9.3b x (1+16.6%)5= $ 20B September 2027 $ 9.3b x (1+16.6%)6= $ 23.4B September 2028 $ 9.3b x (1+16.6%)7= $ 27.3B September 2029 $ 9.3b x (1+16.6%)8= $ 31.8B September 2030 $ 9.3b x (1+16.6%)9= $ 37B September 2031 $ 9.3b x (1+16.6%)10= $ 43.2B Estimated the company’s final value, that is, estimated the company’s market value after ten years. Here, we first calculate the company’s company in the past few years Market rate, That is, the “free cash flow price ratio”, that is, Price to Free Cash Flow, referred to as P/FCF, can judge the company’s stock price growth through this data to increase by free cash flow. P / FCF = Market Capitalization / Free Cash Flow By calculating the P/FCF value of the past five years, the company’s final value can be estimated with the free cash flow of the tenth year. 2021 $ 9.3B $ 232.44B 25 2020 $ 7.3B $ 196.61b 26.9 2019 $ 5.9B $ 99.5B 16.9 2018 $ 6.4B $ 107.35B 16.8 2017 $ 5.2B $ 79B 15.2 Average P/FCF 20.2 Final value = free cash flow in the 10th year X Average P/FCF = $ 43.2B x 20.2 = $ 872.6B Setting a discount rate, this value also requires the data you assume.Here are 8.5%of inflation and other factors.Take 15%as an example: September 2022 $ 10.8B $ 9.42B September 2023 $ 12.6B $ 9.56B September 2024 $ 14.7B $ 9.69b September 2025 $ 17.2B $ 9.83B September 2026 $ 20B $ 9.97B September 2027 $ 23.4B $ 10.1B September 2028 $ 27.3B $ 10.24B September 2029 $ 31.8B $ 10.39b September 2030 $ 37B $ 10.53B September 2031 $ 43.2B $ 10.69B years Company final value The company’s final value is discounted September 2031 $ 872.6B $ 248.1B The company’s inherent value is the sum of the current value of the predicted cash flow and the final value of the final value.As a result, the inherent value of Apple’s company is: Internal value = ten-year cash flow discount + company final value discount = $ 348B The market value of Apple in September 2021 was $ 232.44B, which was lower than its internal value of $ 348B, so it can be considered that Apple’s stock price was underestimated in 2021. For example, you plan to buy a 10 -year Treasury bond of $ 10,000 at a face value.Assuming that the current Rate of 30 years of national debt is 3%, how to use the cash flow discount current law to calculate the inner U.S.Treasury’s inner innerWhat about value? Because the yield of 10 -year Treasury bonds is 3%, you will receive the interest sent to you by the US Treasury Department every year, 10000 x 0.03 = 300, so the interest you get every year is the annual cash flow of cash flow every year. years cash flow ($) First year 300 Second year 300 Third year 300 Fourth year 300 5th year 300 6th year 300 7th year 300 8th year 300 9th year 300 10th year 300 Treasury bonds with a face value of $ 10,000 will eventually bring you a final value of $ 10,000, so the final value of this 10 -year Treasury bond is $ 10,000. years cash flow ($) 10th year 10000 As mentioned earlier, we need to discount the future cash flow to the present.Here, we need to use a discount rate.The simplest method is to consider the current inflation rate.Take R = 8.5%as an example, so that we willYou can discount the annual cash flow to the present.The formula is: Cash flow/(1+r)N so, The cash flow in the first year is: 300/(1+0.085)1 The cash flow of the second year is: 300/(1+0.085)2 EssenceEssenceEssenceEssence The cash flow in the tenth year is: 300/(1+0.085)10 The discount value of the final value of the national debt is: 10000/(1+0.085)10 Therefore, considering the cash flow after discounting is: years cash flow ($) Cash flow ($) First year 300 277 Second year 300 255 Third year 300 235 Fourth year 300 216 5th year 300 200 6th year 300 184 7th year 300 169 8th year 300 156 9th year 300 143 10th year 300 132 Endal value of the 10th year 10000 4423 Therefore, the inherent value of this 10 -year Treasury bond is the sum of all the cash flow in the previous step: Internal value = 277+255+235+216+200+184+169+156+143+132+4423 = $ 6391 You need to invest $ 10,000 for this government bond, but the inherent value of this government bond is only $ 6391.Therefore, this investment is lost and should not invest. Suppose it is planned to invest $ 10,000 to buy a stock, and the stock offering company provides 2%of fixed dividends (each year).You can use the cash flow discount model to determine whether the stock is worth investing. Because the stock issuance company provides a 2%fixed dividend, everyone is expected to get a dividend income of $ 10,000 * 0.02 = $ 200 every year.The dividend investment cash flow that can be obtained is: years cash flow ($) First year 200 Second year 200 Third year 200 Fourth year 200 5th year 200 6th year 200 7th year 200 8th year 200 9th year 200 10th year 200 It is assumed that ten years later, the price of the stock itself has not increased, so after ten years, the stock is still $ $ 10,000. According to factors such as the company’s current development and current inflation rate, set the discount rate R = 10%, thereby calculating the cash flow discount in the next ten years: years cash flow ($) Cash flow ($) First year 200 200 / 1.1 = 181 Second year 200 200 / 1.12= 165 Third year 200 200 / 1.13= 150 Fourth year 200 200 / 1.14= 137 5th year 200 200 / 1.15= 124 6th year 200 200 / 1.16= 113 7th year 200 200 / 1.17= 103 8th year 200 200 / 1.18= 93 9th year 300 200 / 1.19= 85 10th year 200 200 / 1.110= 77 Endal value of the 10th year 10000 10000 / 1.110= 3855 Therefore, according to the cash flow calculated by the previous step, you can calculate the inherent value of this investment: Internal value = 181+165+150+137+124+113+103+93+85+77+ 3855 = $ 5083 For this stock investment, you invested 10,000 US dollars, but the inherent value of this stock is only available $ 5083 EssenceTherefore, this stock is not worth investing.How to use the cash flow discount current method to calculate the internal value of the company’s stock?
Step 1: Find the company’s current free cash flow
Step 2: Forecast the company’s growth rate in the next ten years
years Free cash flow Growth than the previous year Step 2: Forecast the company’s free cash flow in the next ten years
years Free cash flow Step 3: Estimate the company’s final value
years Free cash flow Market value P/FCF Step 4: Consider the discount rate
years Free cash flow Free cash flow
(Fold with 15%)Step 5: Calculate the company’s inherent value
Step 6: Determine whether the company’s valuation is overvalued or underestimated
How to use the cash flow discount current law to calculate the inherent value of US Treasury bonds?Determine whether it is worth investing?
Step 1: Calculate the annual cash flow
Step 2: Calculate the final value of the national debt
Step 3: Consider the discount rate
Step 4: Calculate the intrinsic value of government bonds
Step 5: Determine whether this national debt is worth investing
How to use the cash flow method to calculate dividend investment?
Step 1: Calculate the annual cash flow
Step 2: Calculate the final value of dividend dividends
Step 3: Consider the discount rate
Step 4: Calculate the intrinsic value of dividend dividends
Step 5: Determine whether it is worth investing
What are the advantages of cash flow discount?
What are the disadvantages of the cash flow discount?
