Financial leverage coefficient English is the financial indicator of the degree of Financial Leverage, referred to as DFL, is a financial indicator of a company’s net income or the sensitivity of the capital structure fluctuations and changes from the capital structure.It is one of the company’s important financial risk indicators.Financial leverage usually refers to the cost of financing, that is, after expanding the size of the enterprise through financing liabilities, it is necessary to cost interest for debt expenditure.
Financial leverage coefficients pass the company’s net income change rate or Earnings per share The change rate of change and after-interest rate change is eliminated.The greater the impact of the speed of profit before interest tax.
Different people can use different formulas to calculate the financial leverage coefficient to calculate the degree of impact of its benefit of financial leverage.For example, the rate of net income can be used inside the enterprise, and investors can use the rate of change of income per share to calculate.
Bleak American broker:Transparent securities| | Futu Securities| | Microex Securities| | Tiger securities| | First securities| | Robinhood in| | American Langshang Daquan
Directory of this article
- How to calculate financial leverage coefficients?
- How to calculate Apple’s financial leverage coefficient?
- What are the investment guidance significance of the financial leverage coefficient?
- More investment strategies
How to calculate financial leverage coefficients?
There are three main formulas for calculating the financial leverage coefficient:
1: In addition to the company’s net income change rate, the rate of profit changes before interest taxation, namely:
Financial leverage coefficient = net income change percentage ÷ before interest taxation changes percentage
Degree of Financial Leverage = % CHANGE in Net Income ÷ % Change in EBIT
Among them, net income can be found in the profit and loss statement in the company’s financial report, which is generally calculated by the following company.
Net income = income-sales cost-expenditure
Net income = revenue -COGS -Expenses
Pre-interest taxation & nbsp; = & nbsp; net income & nbsp;+& nbsp; interest expenditure & nbsp;+& nbsp; tax expenditure expenditure
EBit = net intert + interest expense + Income taxes
Net income and tax expenditure can be found in the profit and loss statement in the company’s financial report, and taxes and fees can be found in other income/expenditure tables.
2: In addition to the company’s income change rate per share, the rate of profit changes before interest taxation, namely:
Financial leverage coefficient = percentage percentage of benefits per share / percentage of profit changes before interest tax
DEGREE of Financial Leverage = % CHANGE in Earnings Per Share ÷ % Change in Ebitit
in:
Earnings per share = (net income-preferred dividend) / current number of circulation shares
EPS = (Net Income – Preferred Dividends) / End of Period Shares Outstanding
Priority dividend is a project that needs to be reduced by the establishment of preferred shares.If you set up preferred shares, you do not need to calculate this.
3: Remove the company’s pre-tax profit before tax profit, namely:
Financial leverage coefficient = pre-tax profit / pre-tax profit
DEGREE of Financial Leverage = EBIT / EBT
in:
Pre-tax profit = net income + tax expenditure
EBT = net infle + Income taxes
For the three formulas above:
- The first formula is suitable for the company’s internal use to evaluate the sensitivity of the company’s profitability with the fluctuation of financial leverage;
- The second formula is suitable for the use of investors outside the company to evaluate the sensitivity of shareholders’ income capacity with the fluctuation of the company’s financial leverage;
- The third formula can evaluate the company’s financial leverage within a certain period of time.
how Calculate Apple’s financial leverage coefficient?
This chapter will be released by 10-k released by Apple in September 2021 Financial report Calculate the instance:
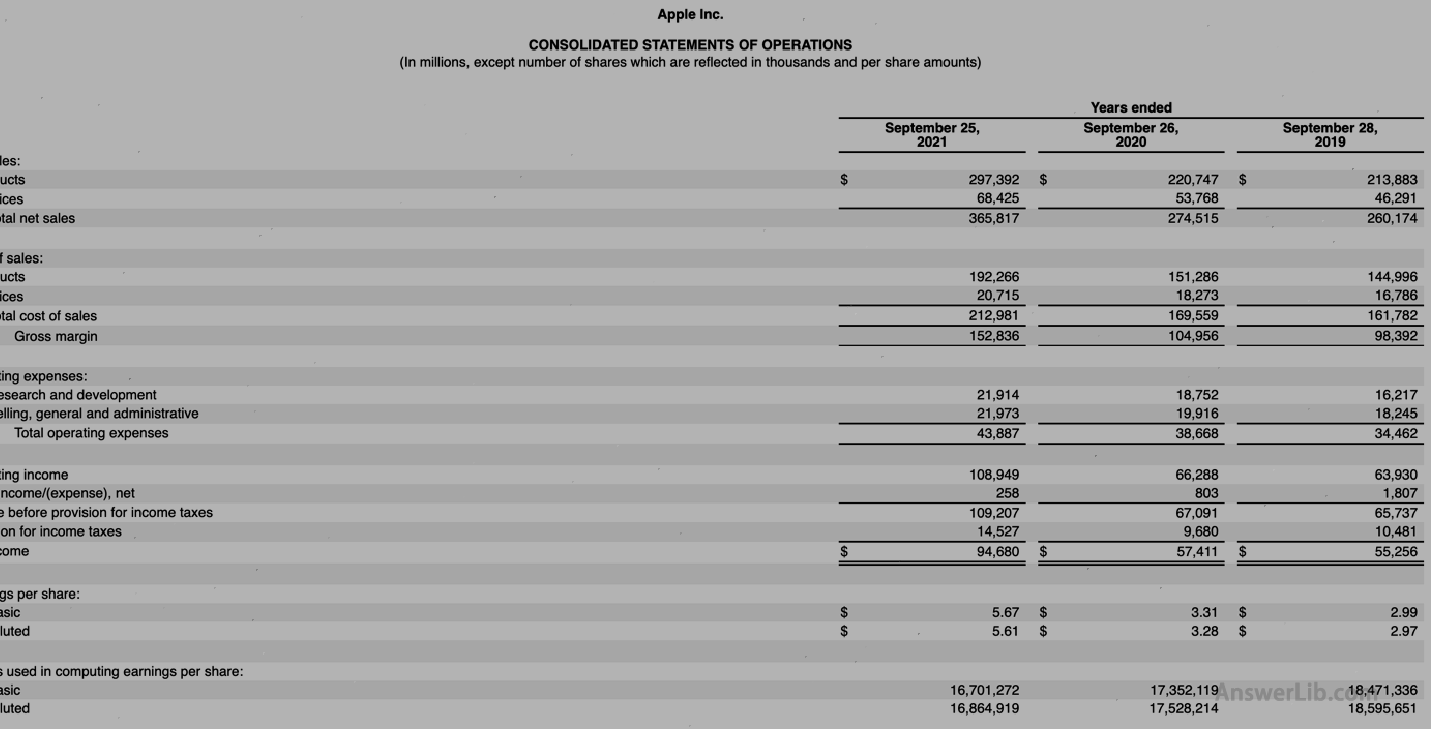
AAPL Financial Report The profit and loss sheet, other income/expenditure tables are shown below:
Profit table:
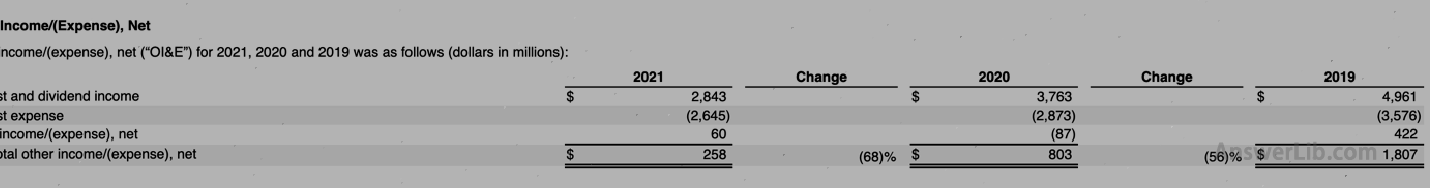
Other income/expenditure table
It can be known from the financial table:
| 2021 $ in mission | 2020 $ in mission | Change rate | |
|---|---|---|---|
Net income / $ | 94,680 | 57,411 | 64.92% |
Interest expenditure / $ | 2,645 | 2,873 |
|
Tax and fee expenditure / $ | 14,527 | 9,680 |
|
EPS / $ | 5.67 | 3.31 | 71.30% |
Ebitit | 111,852 | 69,964 | 59.87% |
EBT | 109,207 | 67,091 | 62.77% |
so:
Formula 1 :
Financial leverage coefficient = net income change percentage ÷ before interest taxation changes percentage
Degree of Financial Leverage = % CHANGE in Net Income ÷ % Change in EBIT
= 64.92% ÷ 59.87%
= 1.08
Formula 2:
Financial leverage coefficient = percentage of changes per share income ÷ before interest tax change percentage of profit changes
DEGREE of Financial Leverage = % CHANGE in Earnings Per Share ÷ % Change in Ebitit
= 1.19
Formula 3:
Financial leverage coefficient = pre-tax profit ÷ before-tax profit
DEGREE of Financial Leverage = EBIT ÷ EBT
= $ 111,852 ÷ $ 109,207
= 1.02
You can see from the calculation results:
For the company’s own profitability, from 2020 to 2021 Financial Year, the financial leverage coefficient is 1.08, that is, when Apple’s financial leverage changes by 1%, its net income will change by 1.08%.
For shareholders’ income, from 2020 to 2021 Financial Year, the financial leverage coefficient is 1.19, that is, when Apple’s financial leverage changes by 1%, the income per share will change by 1.19%.
In the 2021 Financial Year, Apple’s financial leverage coefficient is 1.02, that is, when Apple’s financial leverage changes by 1%during the 2021 Financial Year, its income will change by 1.02%.
What are the investment guidance significance of the financial leverage coefficient?
Through the ratio of financial leverage coefficients, we can only judge the relationship between the company’s current profitability and the relationship between financial leverage.The greater the financial leverage coefficient, the more the profitability of the profit is.Small, the more profitable its profitability is with the changes in financial leverage, and the company’s substantive impact needs to be judged by combining the company’s business ability.
When the company is in a positive stage of development, a higher financial leverage coefficient can bring faster operating income growth to the company.As long as it is properly maintained, this will form a benign development cycle.
When the company is in a slow, stagnant, and even backward development stage, the higher financial leverage coefficient will amplify the company’s financial pressure, increase liabilities, and further drag the company’s profitability.It brings very serious consequences to the company.
Different industries have different average financial leverage coefficients.Usually the banking industry has high financial leverage coefficients, but it is strictly regulated to ensure that relatively stable operating capabilities can be maintained under high leverage coefficients.
The financial leverage coefficient close to zero may usually mean that the company’s credibility is not high, so it cannot smoothly expand the scale of operation through financing liabilities.
