Corporate value multiple English is Enterprise Multiple, which is often marked that EV/EBITDA is often marked.This is a valuation indicator for the company’s valuation, which is used to measure financial indicators with high or low value compared with its stock value compared with other similar companies.
Enterprise value multiple uses company Corporation value(EV) Ebitda Compared with calculation, the corporate value multiple is sometimes called “EBITDA multiple”.
In the calculation of corporate value multiple, corporate value refers to the company’s Market value The sum of the net debt shows the total value of a company including stock sale and debt.EBITDA considers the company’s interest, tax, and depreciation amortization.Because both of them have used a relatively more comprehensive value, the value differences between companies such as different asset types and different tax types have been excluded.Therefore, corporate value multiple can be evaluated by more fair investment or acquisition value evaluation among different companies.Essence
When the corporate value multiple is low, for the company’s own stock price, it is considered to be underestimated, which is usually a signal worth investing.For more different companies, it also shows that the company’s external value is lower than its own profitability.It is a good time for acquisitions, that is, the lower price to buy a company with a good profitability.
Bleak American broker:Ying Diandai 劵| | Futu Moomoo| | Microex Securities| | Tiger securities| | First securities| | Robinhood in
Directory of this article
- How to calculate a corporate value multiple?
- How to calculate Apple’s corporate value multiple?
- What is the investment guidance significance of the corporate value multiple?
- What are the limitations of corporate value multiple?
- What is the difference between corporate value multiple and P/E Ratio?
- More company valuation
How to calculate a corporate value multiple?
Calculation method of corporate value multiple: removing the company’s corporate value before depreciation of the company’s income EBITDA, that is,:
Enterprise multiples = corporate value / interest tax discount pre-amortization pre-amortization benefits
Enterprise Multiple = Enterprise Value / EBITDA
in:
Corporate value refers to the total value of a company, including Market value As well as debt value, the acquisition partner who wants to acquire the company will consider this value to measure the income that you can get after the acquisition.
Corporate value includes the company’s current market value, priority shares, total debt market value, and minority shareholders involved in subsidiaries, and then minus the value after cash and equivalents, that is,:
Corporate value = market value + preferred shares + total debt market value + minority shareholder equity-cash and equivalent
EV = Market Value + Preferred Shares + Total Value of Debt + Minority Interest -Cash and EQUIVALENTS
When calculating the value of the enterprise, its market value uses the number of diluted circulation shares and the current stock price multiplier to calculate.The diluted shares include the number of shares that circulate in the public trading market, the number of potential circulation shares, the number of convertible securities, employee stock options options for employee stock optionsThe total number of circulation shares, including the number of options in the price, the number of options in the price, and the equity permit to reflect the more complete market value.
The number of diluted circulation shares can be in the company’s financial report Profits Find in.
Extraction of interest and tax pre-amortization benefits(EBITDA) is the financial indicator of the company’s profitability, and considers the interest expenses, tax expenditures, and capital depreciation and amortization of the operating process, so as to obtain a relatively complete profitable financial value.
The calculation method of EBITDA is to add taxes, interest expenses and depreciation and amortization fees to the company’s net income, that is:
EBITDA = net income + tax + interest cost + depreciation and amortization
EBitda = network + taxes + interest expense + depreciation & amortization
The data values required for EBITDA can be found in the profit and loss sheet, other income/expenditure tables and cash flow sheets in the company’s financial report.
how Calculate Apple’s corporate value multiple?
This chapter will be released by Apple in September 2021 10-K financial report Calculate the instance:
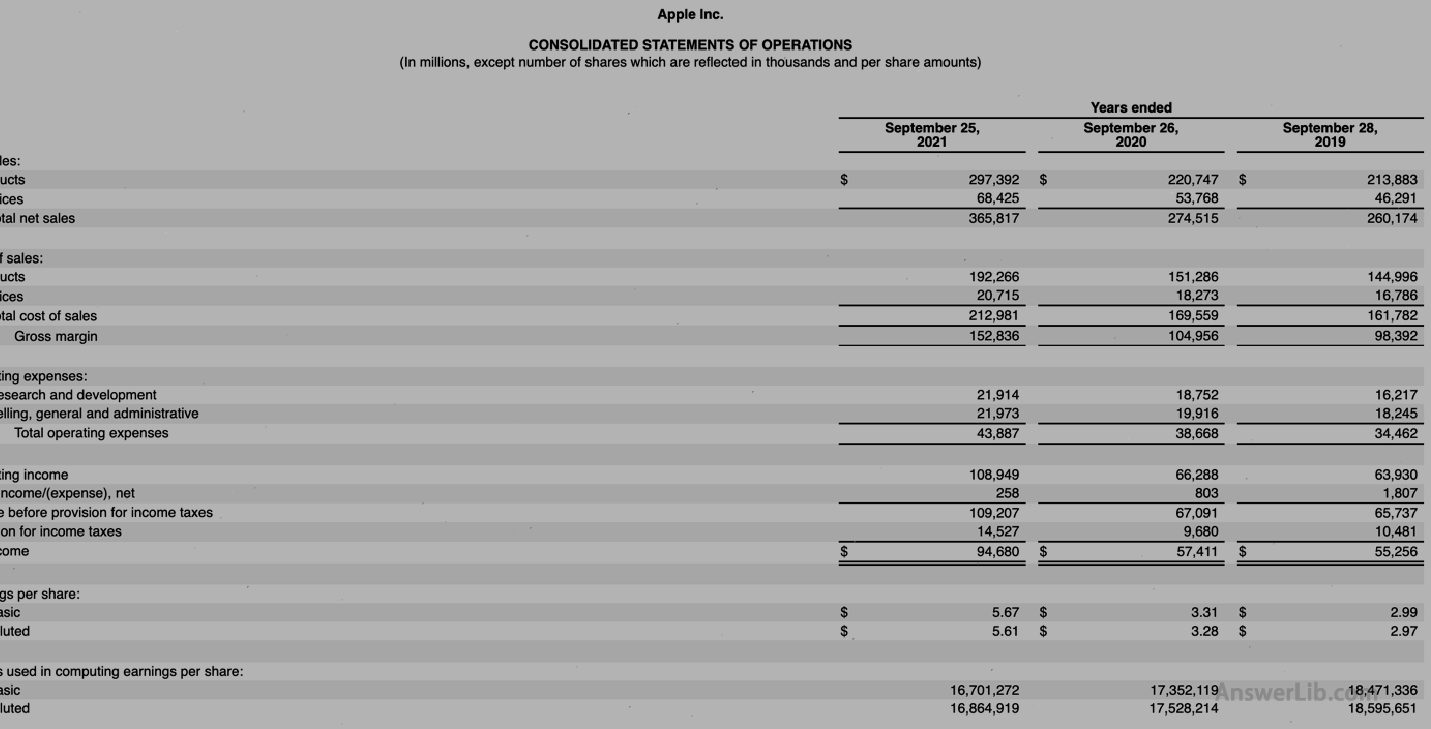
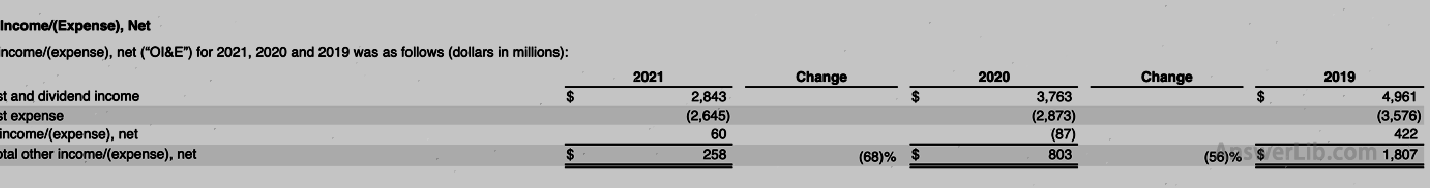
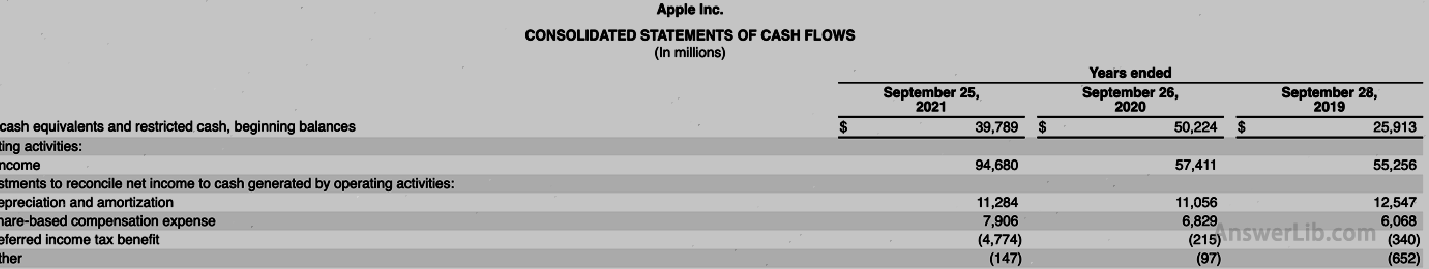
AAPL Financial Report middle Loser, Other income/expenditure form, Cash flow sheet As follows:
Profit or loss statement:
Other income/expenditure table:
Cash flow table:
You can see from the financial statements:
Net income | $ 94,680 m |
Interest expenditure | $ 2,645 m |
tax | $ 14,527 m |
Depreciation amortization | $ 11,284 m |
Dilute circulation stocks | 16,864,919 K shares |
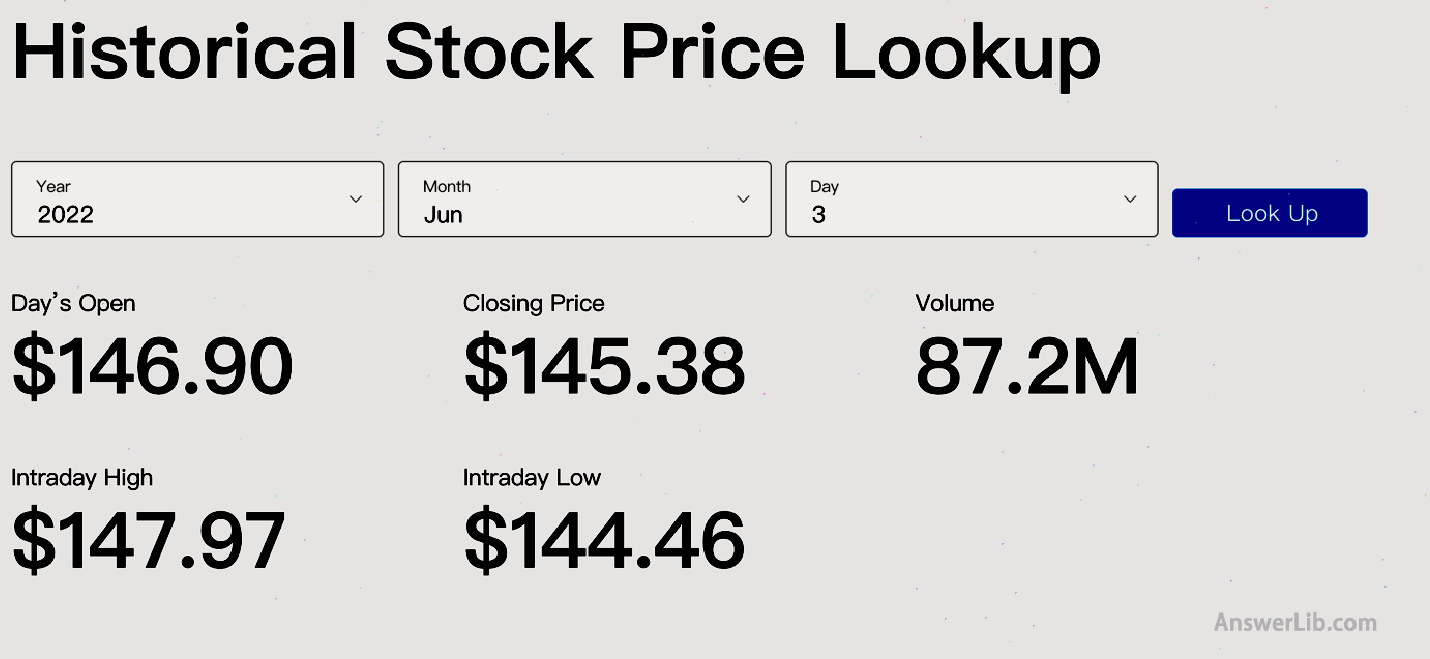
Apple’s current stock price can be in it Investment financial portal website Find it:
Apple has not set up preferred shares and subsidiaries, so there is no preferred shares and a minority shareholder value;
- Total debt: $ 287,912 m
- Cash and cash equivalent value: $ 34,940 m
So the current corporate value of Apple is:
Corporate value = market value+ total debt market value-cash and equivalent
EV = Market Value + Total Value of Debt -Cash and Equivalents
= 16,864,919 k * $ 145.38 + $ 287,912 m – $ 34,940 m
= $ 2,704,794 m
Apple’s current enterprise is worth $ 2,704,794 m
Apple’s 2021 Financial Year of the Financial Year of the Financial Year of the Financial Year of the Financial Year EBITDA is:
EBITDA = net income + tax + interest cost + depreciation and amortization
EBitda = network + taxes + interest expense + depreciation & amortization
= $ 94,680 m + $ 14,527 m + $ 2,645 m + $ 11,284 m
= $ 123,136 m
Apple’s EBITDA in the 2021 Financial Year is $ 123,136 m
Therefore, Apple’s corporate price is multiple:
Enterprise multiples = corporate value / interest tax discount pre-amortization pre-amortization benefits
Enterprise Multiple = Enterprise Value / EBITDA
= $ 2,704,794 m / $ 123,136 m
= 22
That is, Apple’s current corporate value multiple is 22.
What is the investment guidance significance of the corporate value multiple?
Because the company’s value multiples contain the company’s debt and equity, it can more comprehensively reflect the company’s overall business performance.As a result, the corporate value multiple is widely used to evaluate the company’s acquisition value.
When the corporate value multiple is high, it means that the company’s current external value is higher than its profitability.The income obtained after the acquisition may be limited, and it is not enough to offset the acquisition fee.On the contrary, when the company’s value multiple is low, it means that the company’s current external value is lower than its profitability.If you buy it, it is equivalent to spend less money and buy a company with a good profitability.Acquisition objects.Right now:
- Enterprise value multiple is low, which is more suitable for acquisition
- Enterprise value multiple, not suitable for acquisition
When evaluating whether to purchase a company’s stock at the current price, investors can determine whether the stock price is overestimated or underestimated through the corporate value multiple.Generally, when the value multiple of the enterprise is high, it is believed that the current stock price is overestimated.It is not a good time to buy investment.On the contrary, when the corporate value multiple is low, it is generally considered that the current stock price is underestimated, which is a good investment time.Right now:
- The company’s value multiple is low, and the stock price is underestimated.It is the time to buy stocks
- The corporate value multiple is high, and the stock price is overvalued.It is not suitable for buying.
What are the limitations of corporate value multiple?
In actual use, the corporate value multiples are still inadequate:
Although when the value multiple of the enterprise is low, it will think that the company’s stock price is underestimated and is a good investment opportunity.However, if you only look at the corporate value multiple, it may not be able to show the company’s investment return on fundamentals.That is to sayThe value multiple of low enterprise may hide the fact that the company’s negative investment returns, and cause investment decisions to fail.
Enterprise value multiple reflects the relationship between corporate value and profitability.For investors, investment income cannot be obtained.Therefore, some investors prefer to use the ratio between profits and benefits, such as Net profit rate(Net Profit Margin), Profitability Ratios, or the ratio between the price per share and the income per share ( P/E Ratio) Come and check the investment value of the stock more clearly.
EBITDA used in corporate value multiples covers almost all income, but it covers some investment costs.Therefore, investors cannot accurately understand their investment costs from it, so sometimes they tend to use free cash flows to refer to assetsCalculate the cost.
The value multiples of the company can relatively fairly evaluate the investment value between different companies, but for cross-industry companies, there are still evaluation deviations.For example, the same corporate value multiplesFor the technology industry, it may be a very bad financial indicator value.
Therefore, before the final determination of the company’s investment or acquisition value, investors still need to combine a number of fundamental information to better evaluate the company’s investment value and profitability.
What is the difference between corporate value multiple and P/E Ratio?
P / E ratio, English is Price-TO-EARNINGS RATIO, referred to as P/E Ratio.It is the financial value of measuring the relationship between the company’s stock price and the stock income.By eliminating the stock price from the income of each share, that is: P/ERatio = Stock Price / EPS.
When the investment value used to evaluate the company’s stock price, it can be comprehensively evaluated by combining corporate value multiple and P/E value.When evaluating, the higher the ratio.The time, the lower the ratio, indicates that the stock price is underestimated, which is often suitable for buying investment.
The difference between the two is:
| Financial ratio | Corporate value multiple Enterprise Multiple | P / E ratio P/E Ratio |
|---|---|---|
Calculation | Corporate value / interest tax depreciation pre-amortized profit | Stock price / earnings per share |
Ratio indicator | The current value of the company is relative to its profitability compared to its profitability | The current price of stocks for stock income capacity |
Comparison | Evaluate the relationship between the overall value and profitability of the company | Evaluate the relationship between the company’s stock price relative to the stock income |
Scope | Judgment of stock investment timing; Judgment of the time to acquire the company; | The judgment of judging the timing of stock purchase |
More company valuation
- Julian Roberts – Julian Robertson: Father of Tiger Baby
- Explore the 24 first-level dealers of the Federal Reserve
- Important Finance and Investment News
- What is a corporate value multiple?Enterprise Multiple
- What is preferred stock?Preferred stock
- What is the operating leverage coefficient?Degree of Operating Leverage
- What is debt repayment payment rate?DEBT Service Coverage Ratio
- What is capital expenditure?Capital Expendital
- What is the capital asset pricing model?Capital Asset Pricing Model
- What is financial leverage coefficient? Degree of Financial Leverage
