Debt equity ratio, English is DEBT To Equity Ratio It is a measure of a enterprise Financial leverage The important indicator is the proportion of the total debt of the enterprise to the equity financing.
Debt equity ratio, also known as the “Risk Ratio” or “Gearing”, is a leverage ratio.Through comparison of the total debt of listed companies and Total Shareholders’ Equity) The ratio, to evaluate the risks in the financial structure of the listed company.In general, the smaller the company’s debt equity is, the lower its financial leverage, and the better financial situation.
When the ratio of debt equity is high, it means that in the company’s capital structure, the capital proportion of capital obtained through debt is high.On the contrary, if the ratio of debt stocks is low, it means that the company’s capital structure isHigher.
The company’s management and investors, and the bank borrowing party can view the relatively proportion of debt and equity financing used by the company through this ratio.Under normal circumstances, borrowers and creditors will pay more attention to debt equity ratios, because it can provide early warning of financial risks, that is, the possibility of the company cannot fulfill its payment obligations due to the heavier debt.
Bleak American broker:Ying Diandai 劵| | Futu Moomoo| | Microex Securities| | Tiger securities| | First securities| | Robinhood in
Directory of this article
- How to calculate the debt share capital ratio?
- Calculate Apple’s debt share capital ratio
- What is the investment guidance significance of the debt equity ratio?
- More investment strategies
How to calculate the debt share capital ratio?
The basic calculation formula of the debt equity ratio is:
Debt equity ratio = total liabilities / total shareholders’ equity
DEBT To Equity Ratio = Total DEBT / TOTAL SHAREHOLDERS ’Equity
Among them, the total liabilities include the company’s short-term debt and long-term debt, namely:
Total Debt = Short Term DEBT + Long Term Debt
In addition, if the company sets Preferred Equity, because of the special attributes of preferred shares, it has certain compulsory to pay dividends.Therefore, some analysts will use the priority shares as debt calculations instead of shareholders ‘equity, not shareholders’ equityCalculate that different preferred shares calculations will have a great impact on the result of the cash liabilities ratio.
For example: a company has a priority shares of $ 500,000, a total debt that does not include preferred shares, and $ 120 million in total shareholders’ equity without preferred shares.
If the preferred shares are liabilized, the debt equity ratio is:
DEBT To Equity Ratio = ($ 500,000 + $ 1,000,000) / $ 1,200,000 = 1.25
If the preferred shares are included in the total shareholders’ equity, the debt share capital ratio is:
DEBT To Equity Ratio = $ 1,000,000 / ($ 500,000 + $ 1,200,000) = 0.57
In addition, some analysts will use long-term debt to calculate when calculating, because for short-term debt with relatively high liquidity, long-term debt can more truly reflect the company’s debt level.The calculation formula is:
DEBT To Equity Ratio = Long-Term DEBT / Total Shareholders ’Equity
Calculate Apple’s debt share capital ratio
This chapter uses Apple’s latest 10-K financial report Data in China to calculate Apple’s debt share capital ratio:
AAPL’s latest financial report Below Balance sheet The equity table with the shareholders is as follows:
Balance sheet (Balance Sheets) The

Shareholders’ equity statement (Statements of Shareholders ’Equity):
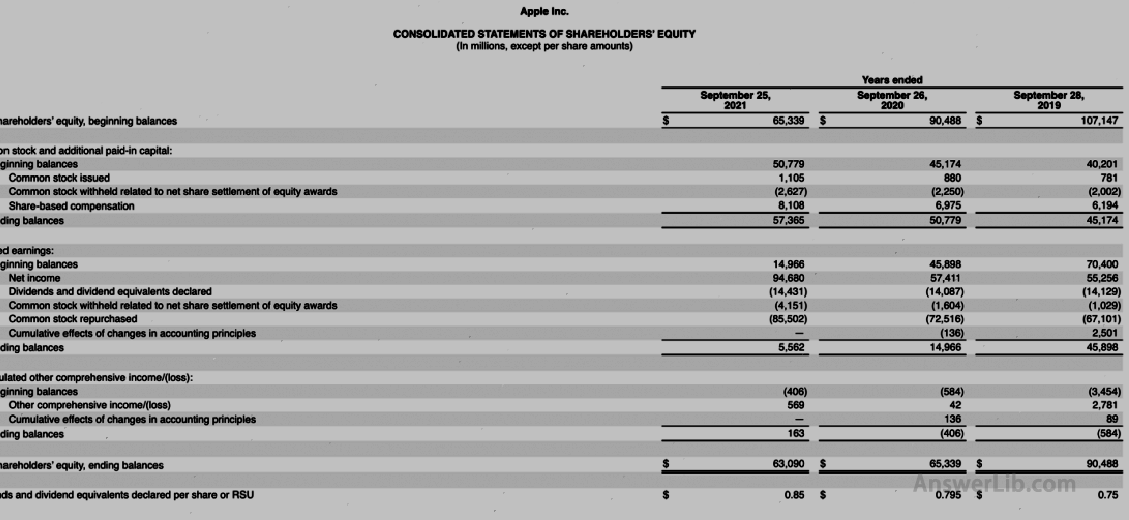
It can be seen from the shareholders ‘equity form that Apple has not set up preferred shares.Therefore, in the calculation of the debt share capital ratio, the total shareholders’ equity is $ 63,090 m.
Use basic calculation formula:
DEBT To Equity Ratio = Total DEBT / TOTAL SHAREHOLDERS ’Equity
= $ 287,912 m / $ 63,090 m
= 4.56
The calculation of the total debt after calculation of the total assets and the total shareholders’ equity is:
Debt to equity ratio = (Assets – Equities) / Total Shareholders ’Equity
= ($ 351002 m – $ 63,090 m) / $ 63,090 m
= 4.56
In other words, in its financial report, Apple records all the liabilities that should be included in the financial statements.
Use long-term debt to calculate the debt share capital ratio:
DEBT To Equity Ratio = Long-Term DEBT / Total Shareholders ’Equity
= $ 162,431 / $ 63,090 m
= 2.58
What is the investment guidance significance of the debt equity ratio?
If the debt equity ratio is 1.5, it means that the company’s equity per $ 1 corresponds to $ 1.50 debt.
Secondly, if the debt share capital ratio is negative, it means that the shareholders’ equity is negative, which means that the company’s current liabilities are greater than their own assets.This is a very dangerous signal for the company or investors, indicating that the company mayFacing the risk of bankruptcy.
What does the debt share capital ratio indicate?
Under normal circumstances, lower debt equity capital means that the company’s operating model is very mature and accumulates a lot of funds.However, for shareholders, it may be considered that the company does not fully use funds to further develop the company’s scale.
The higher debt equity ratio shows that when the company uses shareholders’ investment, it uses a leverage.If the company appears in rapid growth, it means that the company’s operation is smooth.Under the influence of leverage, the investment of shareholders will get more investment.More returns.However, if this situation occurs during the decline of the company, it means that the company’s operations may have greater risks.
It is generally believed that the ratio of the debt equity ratio of about 2 or 2.5 is a better figure.If it is higher than 7, it means that the level of debt is high, which will generally cause vigilance as a lender.
What are the factors that affect the equity ratio of debt?
The first is the company’s shareholder model.If the company sets up preferred shares, as mentioned in the calculation method above, the priority shares will be included in debt or shareholders’ equity due to the subjective factors of analysts.When the preferred shares are included in different categories, it will have a great impact on the final debt share capital ratio.Generally, as the preferred shares holder, the preferred shares will be included in the total shareholders’ equity, rather than the preferred shares holding the preferred shares into the company’s total debt.
Secondly, different types of companies, due to different operating models, usually have a large difference in debt equity ratio.For example, companies whose income is relatively stable and can borrow funds at a low cost, such as public institutional companies, consumer necessities companies, etc., usually their debt share capital ratio is higher.
Then, using long-term debt to calculate the debt equity ratio, it can better reflect the proportion of a company’s overall debt accounted for shareholders’ equity, because the short-term debt’s liquidity is very high, and it is impossible to accurately reflect the calculation purpose of the debt share capital ratio.
