EBIT, English is Earning Before Interest and TAX, Abbreviation Ebitit It is the ability to measure a company that generates profits from its operation without considering interest or taxes.
EBIT is not a prescribed indicator of the GMAP, so there is no calculation method for uniform standards.In general, there are two calculation methods.The first is to add net income and interest expenses and tax expenses.This is the calculation algorithm format that is most consistent with the definition of profit definition before the interest tax; the other is to remove the cost and operating expenses from the income.
Using EBIT, you can obtain the ability of the company to obtain profits through business without considering interest and taxes.Therefore, when comparing companies with different tax models and interest models, using EBIT can better make fair evaluationEssenceIn addition, EBIT is particularly suitable for evaluating capital-intensive companies, because the capital of such companies is usually obtained through debt, and the repayment of debt needs interest.Considering interest expenditure in the company’s operating income, you can better evaluate the company’s companies.Actual profitability.
Bleak American broker:Ying Diandai 劵| | Futu Moomoo| | Microex Securities| | Tiger securities| | First securities| | Robinhood in
Directory of this article
- How to calculate the pre-tax profit?
- Calculate Apple’s pre-interest taxation profit?
- What is the significance of investment guidance before interest taxation?
- What are the advantages of using the profit before interest tax?
- What are the limitations of pre-interest taxation?
- What are the calculations of the pre-tax profit mainly for?
- Join investment discussion group
- More investment strategies
How to calculate the pre-tax profit?
EBIT mainly has two computing formulas:
The first: add interest expenditure and tax expenses back to the company’s net income, that is:
Before interest taxation & nbsp; = & nbsp; net income & nbsp;+& nbsp; interest & nbsp;+& nbsp; taxation
EBit = net intert + interest expense + Income taxes
The second: remove the cost and operating costs from the company’s income, that is:
Before interest taxation & nbsp; = & nbsp; income & nbsp; – & nbsp; sales cost & nbsp; – & nbsp; operating costs
Ebit = revenue − COGS − Operating expenses = Operation Income
in:
- Net income(Net Income) refers to the company’s sales cost, general and management expenses, operating expenses, operating expenses, depreciation, interest, taxes and other expenses;
- Interest expense refers to interest paid by the company to pay for business loans to maintain business operations;
- Income taxes refers to the tax amount that the company must pay for its profit in accordance with US laws in operation;
- Revenue also becomes SALES in some financial statements.It is all income obtained by the company’s operation without deducting any costs;
- COST of GOONS SOLD (COGS) refers to the direct costs of the company used to produce the goods it sells, mainly including materials and labor costs directly used to manufacture products.
- Operating expenses (Operating Expenses) refers to the costs incurred by the company when they use their normal business operations, including rent, equipment, inventory costs, marketing, salary, insurance, and allocating funds allocated to R & D.
The values required for the above calculations can be found from the profit statement and other income/expenditure tables in the financial report issued by the company.
Calculate Apple’s pre-interest taxation profit?
This chapter will be released by Apple in September 2021 10-K financial report Calculate the instance:
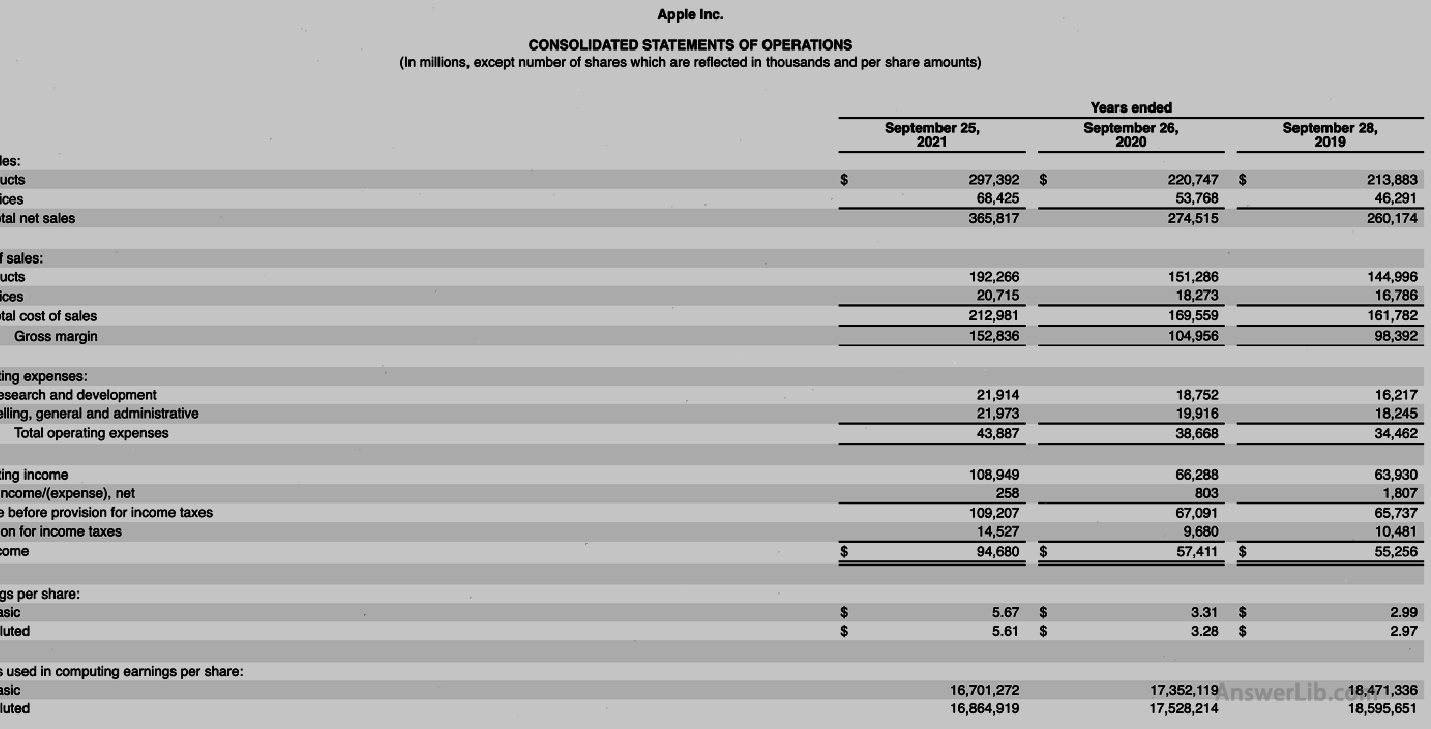
AAPL Financial Report middle Profits, Other income/expenditure tables are shown below:
Profit table:
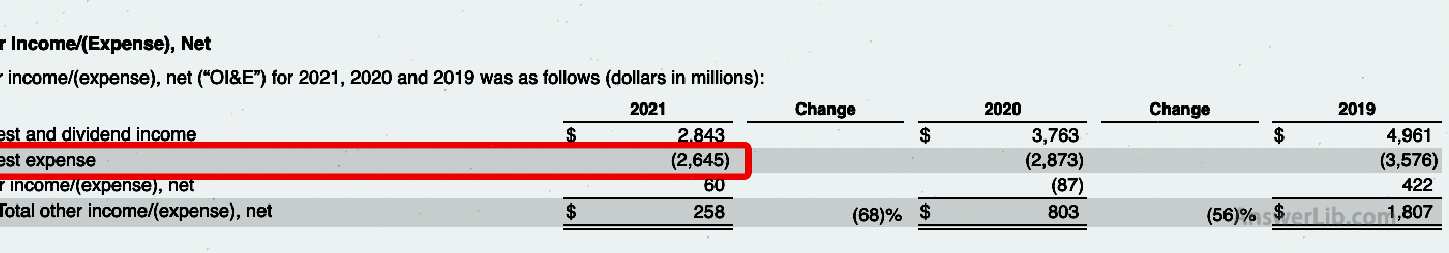
From other income tables, you can find the interest paid by the company:
Net income | $ 94,680 m |
Interest Expense | $ 2,645 m |
Income taxes | $ 14,527 m |
Revenue | $ 365,817 m |
COGS | $ 212,981 m |
Operating expenses | $ 43,887 m |
so:
Through net income, interest paid, and tax amount, EBIT can be calculated:
EBit = net intert + interest expense + Income taxes
= $ 94,680 m + $ 2,645 m + $ 14,527 m
= $ 111,852 m
In addition, if the company’s income comes entirely from operations, then ebit = operating income, from Apple’s profit statement can directly get its operating income = $ 108,949 m.This value is different from the $ 111,842M calculated above.The company also has some other income of $ 2,903M ($ 2,843M + $ 60m), which can be seen from the “other income” table of Table 10-K.
What is the significance of investment guidance before interest taxation?
EBIT numerical represents the profit amount that the company can generate, which is not affected by the company’s loan interest and corporate tax.
For different companies in the same industry, different profit amounts will be generated due to different debt distribution.When using net income to measure the company’s value, there may be deviations.Using EBIT can better measure the investment value of the two companies.
For example, the net income of company A and company B is $ 1,000,000 and $ 800,000, while the interest expenses of the two companies are $ 50,000 and $ 400,000.
When using net income comparison, the performance of the company A seems to be better, but when the interest cost is recovered, the profitability of the company B is obviously better than the company A, because the company B uses loans to create morevalue.
This is the most important role in EBIT in measurement of different companies’ profitability.
What are the advantages of using the profit before interest tax?
The most important value of EBIT is to avoid the impact of non-operating expenses such as taxation and interest to consider the core operating capabilities of a company.
When comparing companies in the same industry and different debt distribution, using EBIT is the most effective measurement indicator, especially for companies that create profitable companies to create profits, using EBIT can be more fair to evaluate corporate value.
At the same time, EBIT is also very suitable for measuring companies’ profitability of different tax conditions.For example, one company enjoys tax discounts and the other does not have it.When using EBIT, it can avoid the measurement results of the company’s profitability.
EBIT is also very suitable for evaluating the profitability of asset-intensive enterprises, because asset-intensive enterprises usually need to prepare assets through debt financing, such as petroleum companies and natural gas companies.Because such companies need to pay a lot of interest because they hold a large amount of debt, when using net income to measure the company’s value, it is impossible to consider the company’s profits through debt.Therefore, when using EBIT to analyzeBusiness ability and profitable potential.
What are the limitations of pre-interest taxation?
Because EBIT is not the standard indicator of GAAP, when calculating, there is no strict industry standard.Different analysts may adjust the value of the EBIT parameter value according to their own needs or enterprise needs.This may be possible.As a result, different analysts will calculate different EBIT values.For example, some analysts or companies may calculate all interest in EBIT, but some companies will only select part of the values based on the different types of interest, which leads to different calculation results of EBIT.
In the calculation of EBIT, the depreciation expenses are included, which will cause a certain evaluation deviation when measured different types of companies.For example, when using EBIT to evaluate a company with a large amount gap between the two fixed assets, in the EBIT calculationMaybe the profitability of the two companies is not much different, but in essence, the profit of the two companies needs to reduce the loss caused by depreciation, so at this time, EBIT cannot accurately evaluate the value of different companies.
What are the calculations of the pre-tax profit mainly for?
At present, there are two main financial ratios to use EBIT for financial analysis, namely:: Interest coverage ratio(Intert Coverage Ratio) and EBIT/EV multiple.
Interest coverage Ratio, the calculation method is EBIT’s ability to measure the company’s ability to pay the company’s unpaid debt with interest costs.
EBIT/EV multiple, EV refers to corporate value Enterprise Value.The calculation method is to divide EBIT with the company’s corporate value.It is an indicator to measure the company’s return yield Earnings yield.
