Profits English is the Income Statement.It is a financial statement that reflects the company’s every quarter or annual profit (or loss), and the cost of spending.
The main targets of the profit statement include the internal company, the potential investors of the company, and other companies in the industry where the company are.An important company financial statement, and Balance sheet and Cash flow sheet Use together to better analyze the fundamentals of listed companies.So, what data are mainly contained in the profit statement and how to understand the profit statement?
Bleak American broker:Ying Diandai 劵| | Futu Moomoo| | Microex Securities| | Tiger securities| | First securities| | Robinhood in
Directory of this article
- What is the profit statement?
- What is the role of profitable statements?
- What are the components of the profit statement?
- What projects may be included in the profit sheet?
- How to read the profit statement?Case of profit table analysis
- How to get the company’s profit statement?
- How to use the profit statement for investment analysis?
- Profit state
- American merchant
- More investment strategies
What is the profit statement?
The profit table English is Income Statement or Earnings Statement, also known as the “profit or loss sheet”, English is the Profit and Loss Statement (P/L Statement).Other English expressions of the profit statement include: Statement of Income or Statement of Operations.
The profit statement shows the company’s income and expenditure in a certain period of time, together with the company’s balance sheet (BALANCE Sheet) and the Cash Flow Statement as the most important data statement of a company’s financial status.
According to the company’s operating model, the profit statement is usually published every quarter (quaterly) or annual (Annually).
The most basic data displayed in the profit statement is the revenue/sales and Expenses.Through these two most basic data, the gross profit of listed companies can be quickly calculated.At the same time, in the profit statement, you will also see some income (Gains) and loss (LOSS) that are not directly related to business.
- Revenue/Sales: The main income or total sales is the income obtained by the company through business activities within the calculation cycle of the profit statement;
- Expenses: In terms of expenses, the company’s expenditure for business activities during the calculation cycle of the profit statement;
- Gains: Income, the income obtained from non-business activities, common ones selling long-term assets, such as selling old trucks, sale subsidiaries, etc.;
- Losses: Losses, expenditure costs outside operations, such as the company sells assets at the price lower than its book value, asset reduction caused by asset reduction, or expenditure costs in response to litigation.
Calculate the final incomant through them, and the net profit is also called “net income”:
Net profit = (income+income)-(cost+loss)
Net income = (revenue + gains) – (expenses + losses)
Based on the statistics or segmentation data used in the profit statement, the profit statement can be divided into Single-Step Income Statement and Multiple-Step Income Statement.
One-step profit statement
Single-step profit statement: List data such as income, expenditure, income, and losses.Most small companies with simpler structures use this profit statement.
Multi-step profit statement
Multi-step profit statements will continue to subdivide the revenue and expenses.For example, revenue can be divided into operating revenues and non-operating revenues, expenses, It is divided into Operating Expenses and Non-Penting Expenses, and combined with income and losses to make a more detailed profit statement.Most large companies use this profit statement.
- Operating income: During the calculation cycle of the profit statement, the income generated by sales in business activities;
- Extra-business income: income obtained outside conventional sales activities, such as interest from banks, rents obtained from rental assets, income from partners, and franchise fees;
- Business expenses: During the company’s operation, the cost of core sales business usually includes sales, general and management costs, depreciation, amortization, and research and development (R & D) wait;
- Outside of business expenses: In the company’s operational activities, activities related to core business, such as interest payment.
What is the role of profitable statements?
The profit statement is important to the company’s management, investors, and loan lenders:
For the company’s management, you can learn from the income of the profit form:
- The company’s operating situation in the current period of time, the amount of profit or loss earned by the company, thereby judging the company’s current operating health, so as to formulate corresponding development strategies;
- The business activities between the company’s main departments, as well as timely discovery of possible operating problems, make adjustments in the operation mode or direction, such as increasing profits by increasing income or reducing costs in the next time period.
For people outside the company, the profit sheet is also very important:
- Investors can understand the company’s ability to control costs in a period of time through the profit statement, earn profitability, and whether the planning decision-making decisions that are distributed by interests can effectively help the company enter the benign operation cycle.Investment;
- The loan lenders will check the profit statement to judge the company’s debt repayment capacity;
- Other companies will understand the cost of the industry in the industry to understand the cost budget in the industry, the reasonable distribution method of interest distribution of interests.
What are the components of the profit statement?
The profit statement is mainly composed of two parts: Revenue/Sales and Expenses.The ultimate goal is to calculate important information such as net income and per share (EPS).
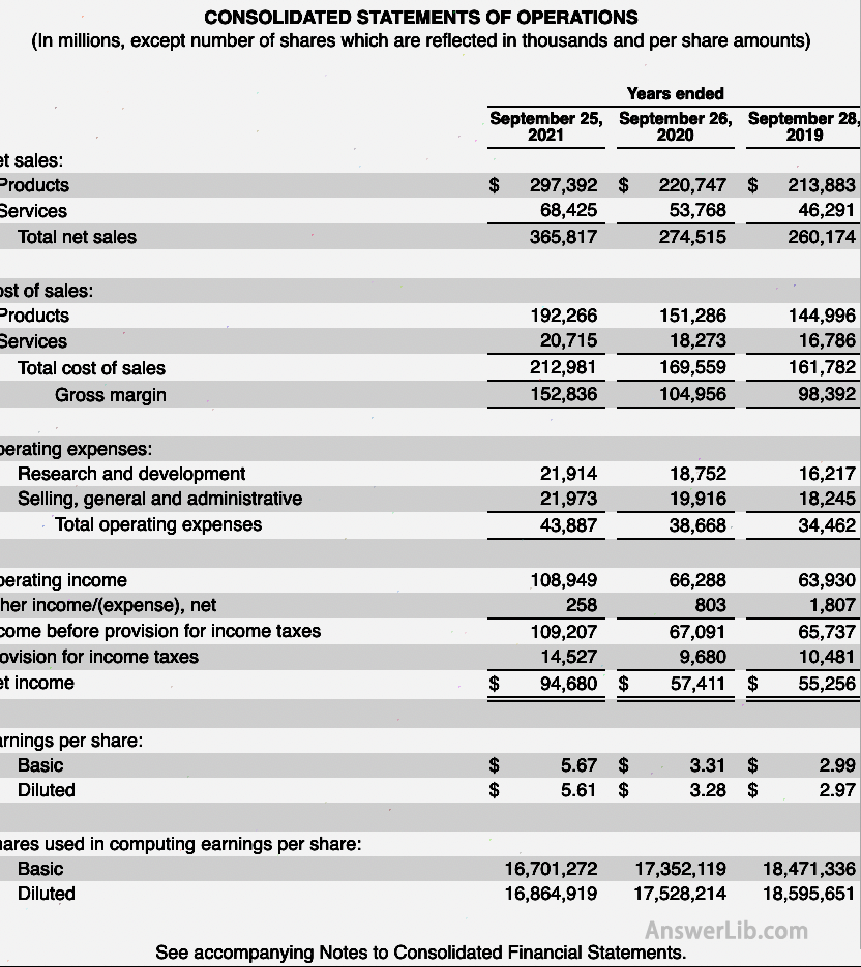
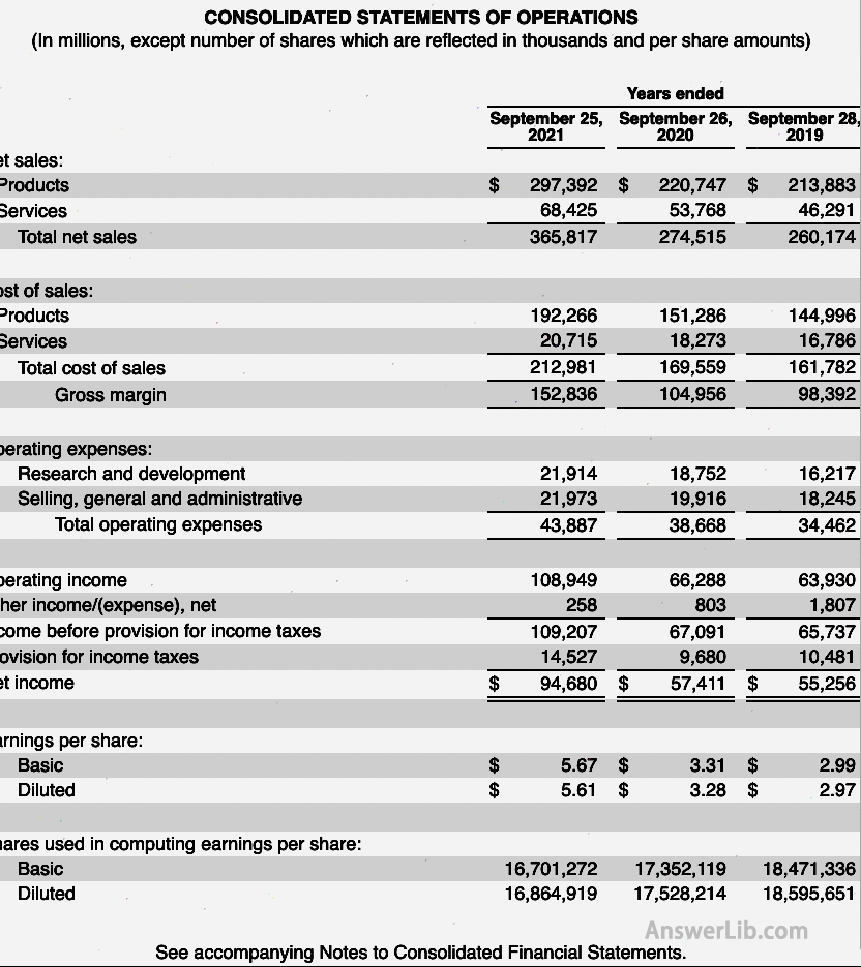
Among them, income and expenses will be subdivided due to different watch-making purposes or the size of the company.Let ’s take Apple’ s 2021 profit statement as an example.Let ’s introduce the common content in the profit statement.
1.Income (Sales/Revenue)
Revenue refers to the company’s revenue, also known as “Sales”, which shows the company’s income obtained by the company’s profit statement calculation cycle.This is the company’s most important source of income for business activities.In the profit sheet, the words “net sales” or “revenue/sales” are often marked.

While the profit statement is marked with income, it is often labeled “income growth rate”:
Increase growth rate (Sales Growth/ Revenue Growth)
Income growth rate English is Sales Growth or Revenue Growth.It is the ratio of income growth to the current total income.In the table, the company’s revenue in 2017 was $ 228.57B, and the revenue in 2018 was $ 265.81B, so
Sales Growth = ($ 265.81B-$ 228.57B)/$ 228.57b*100%= 16.29%
Therefore, the income growth rate is 16.29%
2.Cost cost (COGS)
The cost of selling goods is the COSTS of Goods Sold, referred to as COGS.The cost that the company needs to spend in the process of manufacturing and selling products is often marked as “Cost Sales” or “COGS” in the profit sheet.

When calculating the cost of sales, there is a sales cost called COGS Excluding D & A.
COGS Excluding D & A
Do not include the cost of sales, including depreciation and amortization.Depreciation generally refers to the value loss caused by fixed assets due to depreciation, such as equipment depreciation.The amortization fee is an intangible asset and deferred assets in installments within a certain period of time.
3.gross income (GROSS Income)
The English English English is a Group or GROSS Income.It is the remaining income after minus the cost of selling goods.The calculation is as follows:
Fool profit = income-sales cost
Gross income = revenue -COGS
In the Apple profit sheet, there is a small error.The gross profit should be used in the Gross Income instead of the Gross Margin.GROSS Income is a specific value, and Gross Margin is a ratio, which is often expressed by percentage.
Through the gross profit above, we can calculate the gross profit growth rate and gross profit margin between different years.
GROSS Income Growth
The growth rate of gross profit growth rate is the ratio of gross income group.
In the table, the company’s gross profit was $ 86.87B in 2017, and the profit in 2018 was $ 101.98B
Sales Growth = ($ 101.98b-$ 86.87B)/$ 86.87b*100%= 17.4%
That is, an increase of 17.4%
Growth Profit Margin
The English English English is Growth Profit Margin, which shows the ratio of gross profit for income.The calculation formula is as follows:
Gross profit margin = gross profit/income
Gross profit margin = Gross Profit / Revenue
From the above profit form, it can be seen that the company’s gross profit in 2021 is $ 152.84B, and the income is $ 365.82B, so
Gross profit margin = $ 152.84B/$ 365.82B = 41.78%
4.Business expenses (OPEX)
Operating expenses English is Operating Expenses, referred to as OPEX, which refers to the company’s various operating expenses, including employee salary, non-carried -up rent, daily management, advertising marketing, scientific research and innovation costs, and so on.

Here we will focus on the two in the operating expenses:
Research & Development
R & D expenses, the cost of the company’s research and development part is usually one of the main expenses of some high-tech companies.
Sg & a expense
SG & A Expense is the abbreviation of Selling, General and Administrative Expense, refers to sales costs, comprehensive expenses, and administrative management costs.It is part of operating costs, but it is different from the previous sales cost COGS.SG & A costs the following parts:
Through SG & A Expense, SGA Growth can be calculated, indicating the ratio of the two-year SGA cost difference to the SGA cost of the previous year.According to the above profit statement, Apple’s 2018 compared to the 2017 SGA Growth as follows:
SGA Growth = ($ 30.94B-$ 26.84B)/$ 26.84b*100%= 15.27%
5.Operating profit
Operating profit English is Operating Income or Operating Profit.It is the remaining profit after removing operating expenses from gross profit.The calculation formula is as follows:
Business profit = gross profit-business costs
Operating infy = gross income -Operating expenses

6.Other Income/(Expense)
Other INCOME/(Expense) refers to other income other than operating profit, or expenses other than operating expenses.For example, the company’s expenses spent when they encounter litigation.

7.Income Before Provision for Income Taxes)
The English profit of pre-tax profit is Earnings Before Taxes, referred to as EBT, and sometimes it is also described as “Income Before Provision for Income Taxes”, which refers to the income of not deducting taxes (TAX).

8.Estimated income tax
Estimated income tax in English is Proveisions for Income Taxes, which refers to the tax that the company needs to pay for profits

9.Net Income
Net Income is net profit.It is a part of the company’s profit except all costs and an important indicator of a company’s profitability.
10.Eap per share (EPS)
Earnings per share, also known as “net profit of US stocks” or “profit per share”, English is Earnings Per Share, referred to as EPS, refers to the net profit per share, also known as “US stock income” or “profit per share”, indicating that it indicatesIn the public trading market, the company’s income can bring to shareholders per share.The calculation formula is as follows:
Earnings per share = net profit / circulation shares
EPS = Net Income / Number of Shares Outstanding
The income per share can be divided into two types: basic earnings per share and dilution per share:
1) Basic US stock income, English is EPS BASIC.When calculating, the number of circulating shares used only considers all the company’s basic shares outstanding.The calculation formula is as follows:
EPS (BASIC) = Net Income / Number of Basic Shares Outstanding
2) Dilute the income per share.The English is EPS DILUTED.When calculating, the number of circulating shares used includes all the dilution shares, including all circulating stocks, employee stocks, and shares.The calculation formula is as follows:
EPS (DILUTED) = Net Income / Number of Diluted Basic Shares Outstanding
What projects may be included in the profit sheet?
In addition to the above important content, you may also see the following projects in the profit statement:
Pre-interest taxation profit (EBIT)
Profit profit before interest taxation is Earnings Before Interest and Taxes, referred to as EBIT, which is worth deducting interest before interest and taxes.The calculation formula is as follows:
Profit of interest before interest tax = net income+interest+taxes
EBIT = Net Income + Interest + TAX
EBITDA before tax depreciation and amortization (EBITDA)
Profit English before tax depreciation and amortization is Earnings Before Interest, TAXES, DE-PRECIATION and AMORTIZATION, referred to as EBITDA, which is an income of unsatisfactory interest, depreciation, taxes and amortization.
Consolidated Net Income
Combined net profit English is the consolidated net income.When the company has a subsidiary, add the net profit of the subsidiaries and the parent company as the merger of net profit
Preferred dividend preferred divisionnds
Priority shares English is Preferred Dividends.
How to read the profit statement?Case of profit table analysis
This chapter uses Amazon’s profit statement for nearly three years to interpret the important information of the profit statement:
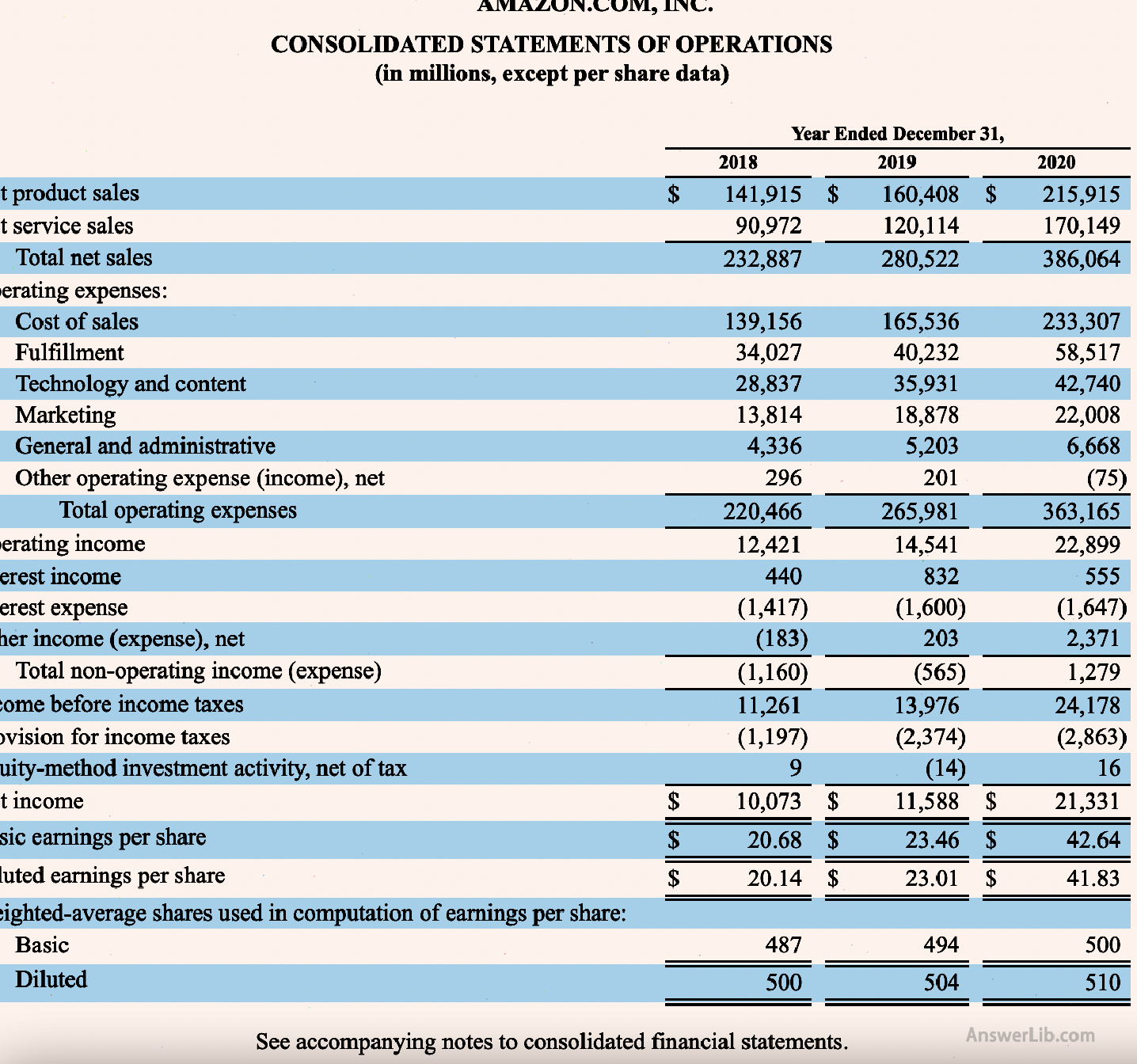
Amazon’s income is mainly composed of selling products and providing services.The total revenue of 2018 is $ 232,887, in 2019 for $ 280,522, and 20120 is $ 386,064.
Amazon’s operating costs include sales costs, marketing fees, technical department costs, and conventional management expenses.The total sales expenses for three years are: $ 220, 466, $ 265,981, $ 363,165.
In terms of operating income, three years are $ 12,421, $ 14,541, and $ 22,899.
In terms of non-operating income/expenditure, there are mainly interest income, interest expenditure and other income/expenditure composition.In 2018, expenditure is $ 1,160, expenditure in 2019 is $ 565, and revenue in 2019 is $ 1,279.
Therefore, the three-year pre-tax income is: $ 12,421 — $ 1,160 = $ 11,261, $ 14,541 — $ 565 = $ 13,976, $ 22,899 + $ 1,279 = $ 24,178, and it continues to grow in three years.
After minusing various taxes and fees, the three-year net income was $ 10,073, $ 11,588, and $ 21,331, respectively.
For market circulation stocks at the time, the basic income of three years was: $ 20.68, $ 23.46, and $ 42.64.
As a result, for companies with large scale, more detailed multi-step profit sheet is needed to completely show information such as all profits and expenses of the company.
How to get the company’s profit statement?
For listed companies, the profit statement is a public financial statement.You can view the profit statement of a company through various forms.For example, directly search for “Investor Relations Site: plus the company website”, or from the No.1 on the Google, or from No.1Three-party financial website, such as MarketWatch.com, Yahoo Finance, MONINGSTAR, MSN Money and other search companies, view its profit statement, or search for the company name on the SEC website, and then view its profit statement.
On the homepage or SEC of the boss company, you are likely to find a company 10-K table.The 10-K table is a comprehensive report on its financial performance that all listed companies in the United States must submit each year.The profit statement.
According to the requirements of the Federal Securities Law, listed companies must continue to disclose 10-K information information each year.The annual report of Table 10-K comprehensively overlook the company’s business and financial status, and also includes audited financial statements.According to the US Securities and Exchange Commission, companies with 700 million U.S.dollars or above public shares must submit 10-K within 60 days after their fiscal year.Companies with circulation between $ 75 million and $ 700 million are 75 days, while companies with circulation less than $ 75 million must be submitted within 90 days.
Method 1: Use Google Search
Taking the profit statement of Apple as an example, using Google Search, the Investor Relations found on the official website of the listed company, the specific steps are as follows:
- Step 1: Search in Google, enter Investor Relations Site: Apple.com
- Step 2: From the search results, find the 10-K form of the Apple homepage, as shown below:
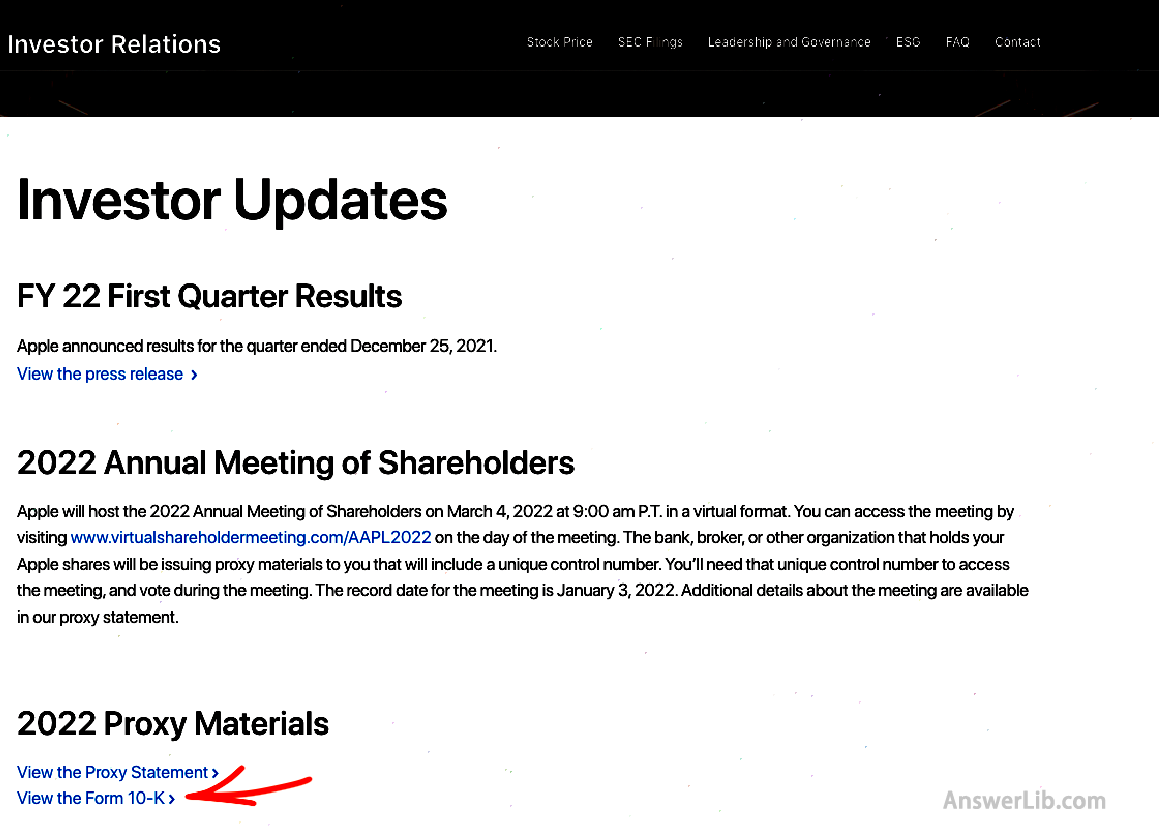
- Step 3: Click Table 10-K to find the corresponding profit form part from the form:
Method 2: Find from the third party’s financial website
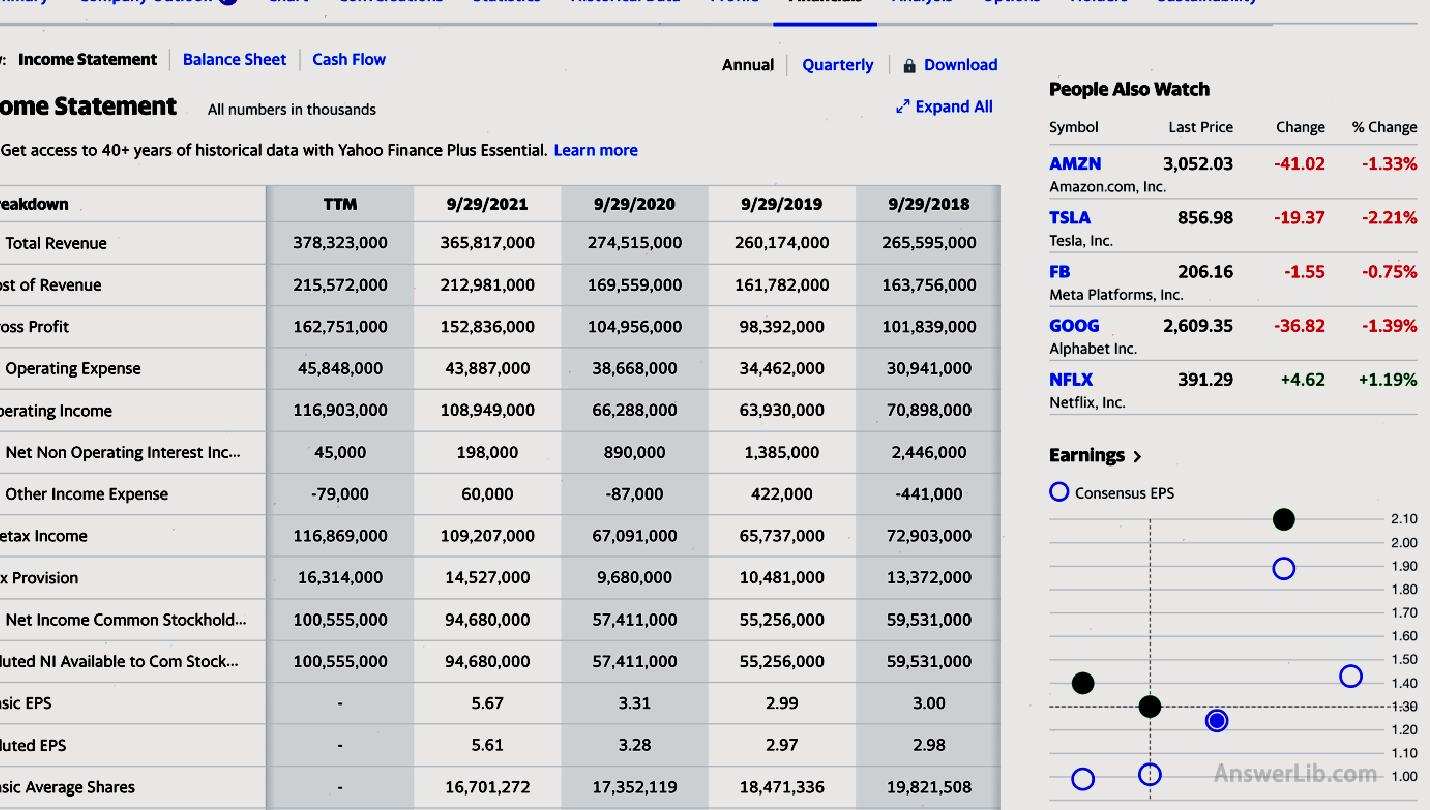
These websites include MarketWatch.com, Yahoo Finance, Morningstar, MSN Money, Reuters, etc.The following take Yahoo Finance as an example:
- Step 1: Login Yahoo Finance main station Enter the company name or TICKER on the search box on the top of the page.For example, for Apple, you can enter AAPL
- Step 2: After entering the company’s data page, click Financials in the data bar
- Step 3: Then you can view the company’s disclosure financial data in recent years:
Method 3: Find the 10-K form of a listed company from the SEC main station
You can enter the SEC main station through Google search, or you can directly enter SEC main station On the search page, enter the company name to check the company’s multiple public financial statements.
- Use Google to search and use the keyword “Apple Income Statement Site: SEC.GOV”.The search results are shown below:
- Click the first option to find Apple’s 10-K table.
How to use the profit statement for investment analysis?
The profit statement can not only directly display the company’s income and expenditure within a certain period of time.Using these data, in addition to calculating the Gross Profit Margin and EPS, you can also calculate and analyze the value of the company’s operating indicators:
Profit margin ( Profit Margin)
The profit margin is Profit Margin, which is the ratio of net income to net income after minusing all expenses required for net sales.It can be divided into pre-tax profit margin and after-tax profit based on whether tax and fees are subtracted.
Calculation formula | Profit margin = profit / total income |
Numerical | The higher the profit margin, the higher the capacity of the sales process into actual profit during the company’s operation. |
Exemplary example | The net sales of a company are $ 100,000, the sales cost is $ 60,000, the SG & A cost is $ 10,000, the interest is $ 5,000, and the taxes are $ 5,000. Pre-tax profit margin = [$ 100,000- ($ 60,000+$ 10,000+$ 5,000)] / $ 100,000 = 0.25 After-tax profit margin = [$ 100,000- ($ 60,000+$ 10,000+$ 5,000+$ 5,000)] / $ 100,000 = 0.20 |
Business profit margin ( Operating margin)
Operating profit margin English is Operating Margin.It is the judgment value of the company’s high or low interest efficiency through business.It is the ratio of the company’s operating income to all income.
Calculation formula | Business profit margin = operating income / income |
Numerical | The higher the operating profit margin, the higher the proportion of profits in the company’s income, and the higher the efficiency of the company’s benefit through sales. |
Exemplary example | The company’s income is $ 50,000, and the operating income is $ 40,000 Business profit margin = $ 40,000 / $ 50,000 = 0.8 |
P / E ratio ( P/E Ratio)
The price-earnings ratio English is P/E Ratio.It can valuation the stock sold by the company’s sale through this number.The value of P/E ratio means that investors need to pay for each US dollar income.
Calculation formula | P / E ratio = stock price / earnings per share |
Numerical | The higher the price-earnings ratio value, the higher the amount to be paid for a dollar earning, the less income will be finally obtained. |
Exemplary example | The company’s current stock price is $ 10, and the earnings per share are $ 16 P/E ratio = $ 10/$ 16 = 0.625 |
Interest coverage ratio ( Times Internet Earned)
Interest guarantee multiple English is Times Interest Earnet, the ratio of EBIT to interest costs, and the amount of interest rate standard for the company’s payment of interest capabilities.
Calculation formula | Interest guarantee multiple = EBIT / Interest cost |
Numerical | The higher the interest guarantee multiples, the more the company is capable of paying the interest, and the loan lender is more willing to lend the money to a company with a high interest guarantee multiple. |
Exemplary example | The company’s EBIT is $ 50,000, and the interest fee is $ 2,000 Interest guarantee multiple = $ 50,000 / $ 2,000 = 25 |
Return on equity
In return of equity, English is Return On Equity.It is one of the most important reference values for investors to choose investment objects.It marks that the company transforms the investment of shareholders into profit efficiency.
Calculation formula | Back to equity = net profit / shareholders’ equity |
Numerical | The higher the return on the equity return, it means that the company can convert shareholders’ investment into profits more efficiently. |
Asset return rate ( Return on assets)
Capital returns English is Return on assets, and it is an important indicator of a company’s management and production capacity.
Calculation formula | Asset yield = net profit / total asset |
Numerical | The higher the asset yield, the higher the ability company to make profits, and the better the ability to save funds at the same time. |
Capital turnover rate ( Asset Turnover Ratio)
The capital turnover English is the Asset Turnover Ratio, which shows that the company’s operating income can generate the operating income of each US dollar asset, representing the company’s operating income capacity.
Calculation formula | Asset turnover rate = operating income / total assets |
Numerical | The higher the value, the higher the efficiency of the company’s transformation of assets into income, and the ideal the operating capacity. |
Profit state
The profit statement and the balance sheet are the two most important reports in a company’s financial statements.Through these two forms, you can understand the assets and debts of a company.According to the data table comparison of different periodsOperations, etc.But there are differences between them:
Different goals
- The profit statement is used to show the income and expenditure that the company can generate during a period of time, expressing the company’s business performance in a certain period of time;
- The balance sheet represents the assets of the company, the debt owed, and the equity owned by shareholders at a certain time point.
The calculation time is different
- Increase and expenditure for a period of time when the profit statement is used;
- The balance sheet reflects the assets, debts and shareholders’ equity at the specific time point.
Different use
- The purpose of the profit statement is to help evaluate whether the enterprise is profitable within a certain period of time, and the difference in profitability between different departments in the operating structure;
- The purpose of the balance sheet is to help evaluate whether enterprises have sufficient ability to fulfill their debt obligations.
Different calculation methods for account income
When the company’s long-term partners proposed to make orders on October 1, and then pay the order fee on November 1st.
- If the meter dates of the profit statement are from October 1st to October 31st, because the order is not received, it will not enter the profit statement;
- If the table dates of the balance sheet is from October 1st to October 31st, this order will be included in the company’s assets.
American merchant
American securities firms ranking and comparison [2023] 12 US securities firms recommend
